Introduction
Navigating the complex landscape of entrepreneurship often leads to a pivotal question: should one establish a Limited Liability Company (LLC) or secure a business license first? Both options are essential for legitimizing a business, yet they serve distinct purposes that can significantly impact an entrepreneur’s journey. Understanding these differences is crucial, as making the wrong choice can lead to legal complications or financial setbacks. Entrepreneurs must consider various factors when deciding the order of these foundational steps, ensuring compliance while maximizing their business potential.
Define LLC and Business License: Key Differences
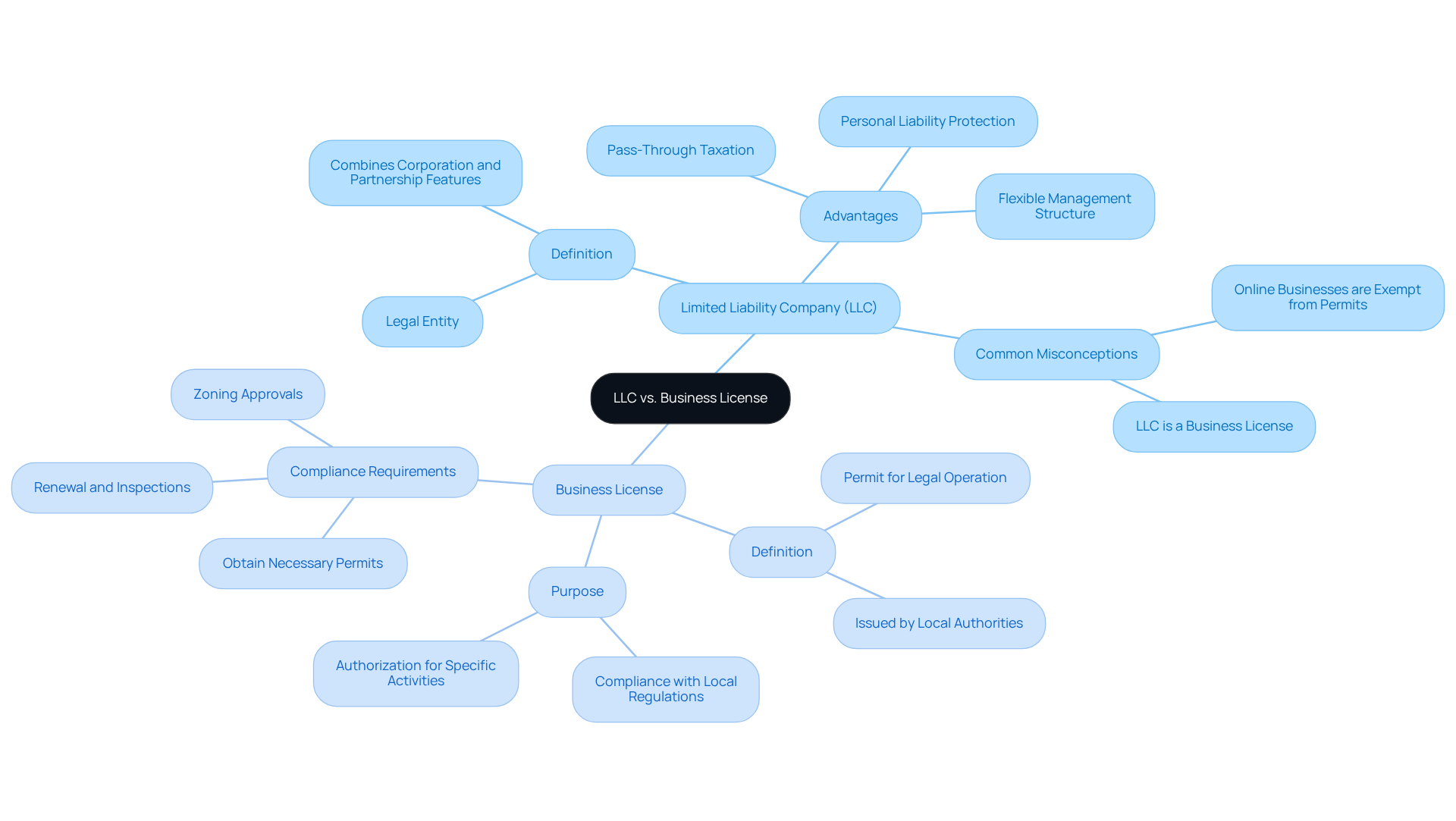
A Limited Liability Company (LLC) serves as a legal entity that merges the advantages of both corporations and partnerships, offering personal liability protection to its owners. This means that personal assets are generally shielded from company debts and lawsuits, making LLCs a preferred choice for small and medium-sized enterprises. In contrast, a commercial permit is an authorization granted by local government officials, permitting legal operation within a designated area. While an LLC establishes the legal framework for a business, a permit is essential for compliance with local regulations and facilitates the execution of specific commercial activities.
As of 2026, the number of businesses operating under the LLC structure continues to rise, reflecting its attractiveness due to flexibility and liability protection. For example, entrepreneurs in regulated sectors, such as restaurants or healthcare, must navigate both LLC formation and local licensing requirements to ensure compliance and operational success. A common oversight among startups is the assumption that they can handle everything by getting a business license or LLC first; they often overlook the necessity of obtaining the appropriate permits, which can lead to penalties or operational disruptions.
Experts emphasize the importance of understanding the distinctions between limited liability companies and operating permits. Entrepreneurs are encouraged to seek legal counsel when expanding into new markets or operating in regulated industries to avoid costly errors. By recognizing the unique roles of LLCs and operating permits, entrepreneurs can better protect their investments and pave a smoother path to entrepreneurial success.
Determine Which to Prioritize: LLC or Business License?
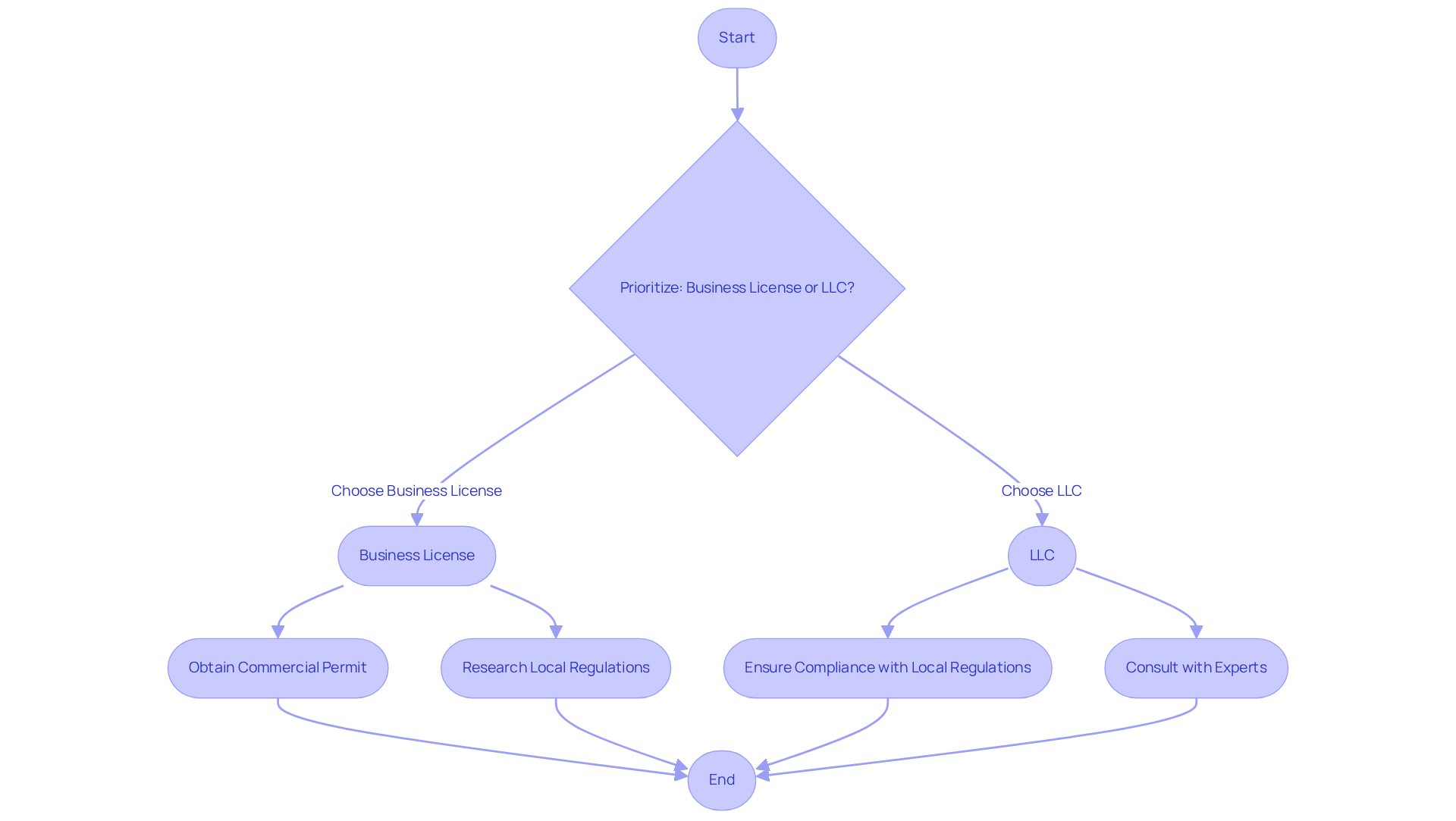
When embarking on a new venture, entrepreneurs frequently face the critical decision of whether to prioritize a business license or LLC first. It is generally advisable to prioritize obtaining a business license or LLC first, as this provides a legal framework that safeguards personal assets, which is essential for mitigating risks associated with business operations. Limited liability companies are favored by entrepreneurs seeking liability protection, as they offer tax benefits and a flexible management structure – key elements for startups across various industries, including e-commerce and gaming.
Once the LLC is established, it is typically more straightforward to obtain a commercial permit, especially after securing the business license or LLC first, as the company is recognized as a legitimate entity. This sequence not only enhances credibility with customers and investors but also simplifies adherence to local regulations. Many entrepreneurs have successfully formed their limited liability companies or obtained their business license or LLC first before applying for the necessary permits, allowing them to operate legally and with confidence.
However, it is crucial to recognize that specific requirements can vary significantly by state and industry. Entrepreneurs must thoroughly research local regulations to ensure compliance with all necessary criteria, as neglecting licensing requirements can result in fines or operational interruptions. By understanding the benefits of forming a business license or LLC first and consulting with experts at Social Enterprises, entrepreneurs can more effectively navigate the complexities of launching their ventures, including investment strategies and tax compliance.
Compare Benefits and Drawbacks: LLC vs. Business License
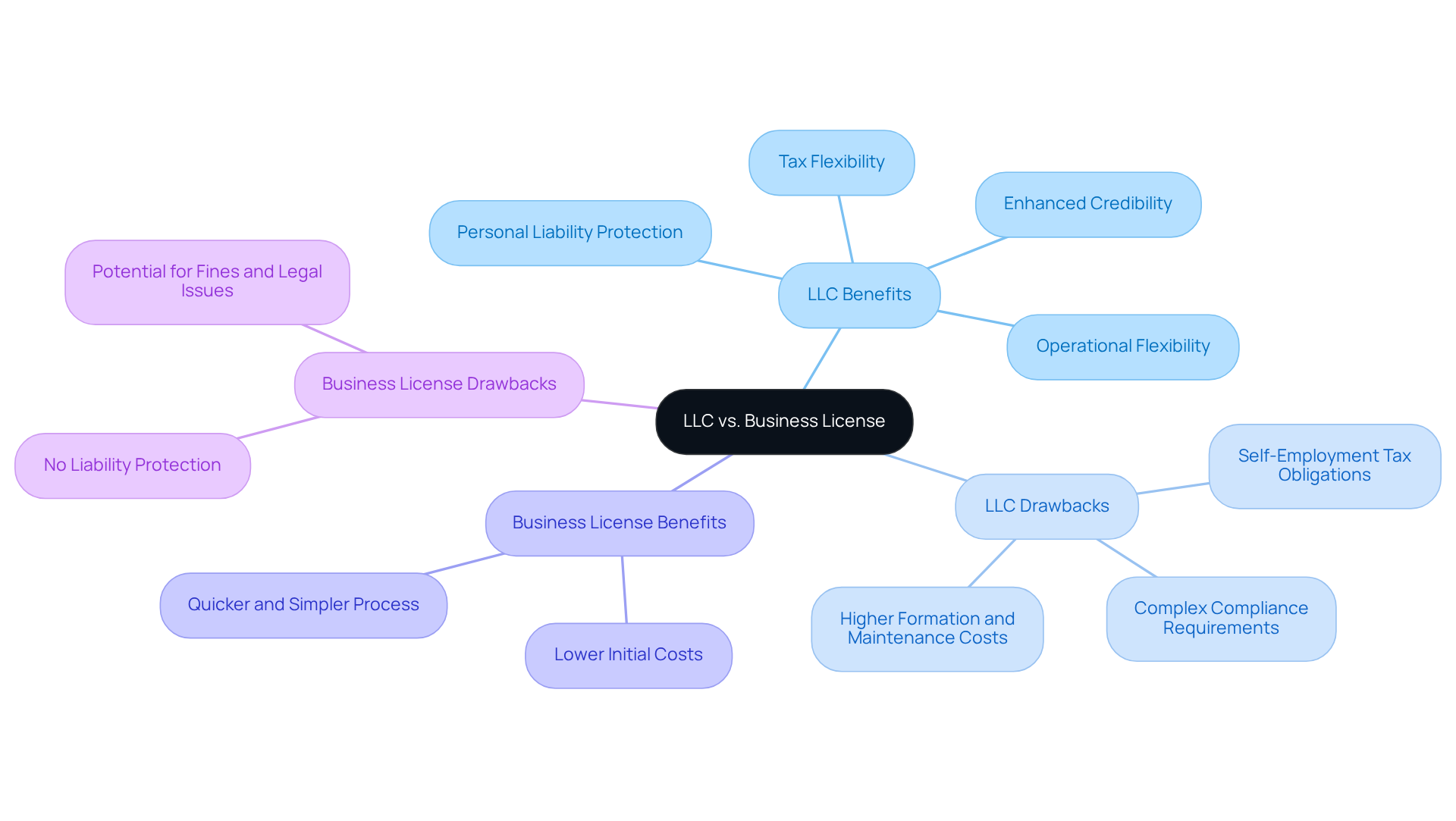
Entrepreneurs must carefully consider the distinct advantages and disadvantages of having a business license or LLC first. Establishing an LLC provides significant benefits, including personal liability protection, which safeguards owners from debts and obligations associated with their business. This structure also offers tax flexibility, allowing profits to pass through to personal tax returns, thereby avoiding double taxation. Furthermore, LLCs enhance credibility with customers and suppliers, indicating that the organization is a legitimate entity. However, the formation and maintenance of an LLC require more paperwork and ongoing compliance obligations, such as filing annual reports and paying state-specific fees, which can vary from $70 to over $800 annually, depending on the state.
In contrast, obtaining a commercial permit is generally a quicker and simpler process, often requiring less paperwork and incurring lower costs. However, it does not offer any liability protection, leaving owners personally vulnerable to business risks. Operating without the necessary licenses can result in substantial fines and legal complications, highlighting the critical importance of compliance.
Entrepreneurs, particularly in the e-commerce sector, should reflect on real-world examples where limited liability companies have proven advantageous. For instance, many small business owners favor LLCs for their operational flexibility and the ability to separate personal and corporate finances, which is vital for maintaining liability protection. Conversely, the challenges associated with LLCs, such as the complexity of compliance and potential self-employment tax obligations, must also be considered. Ultimately, the decision should be made regarding whether to prioritize a business license or LLC first, aligning with the entrepreneur’s specific needs, risk tolerance, and long-term goals.
Outline Steps for Obtaining an LLC and Business License
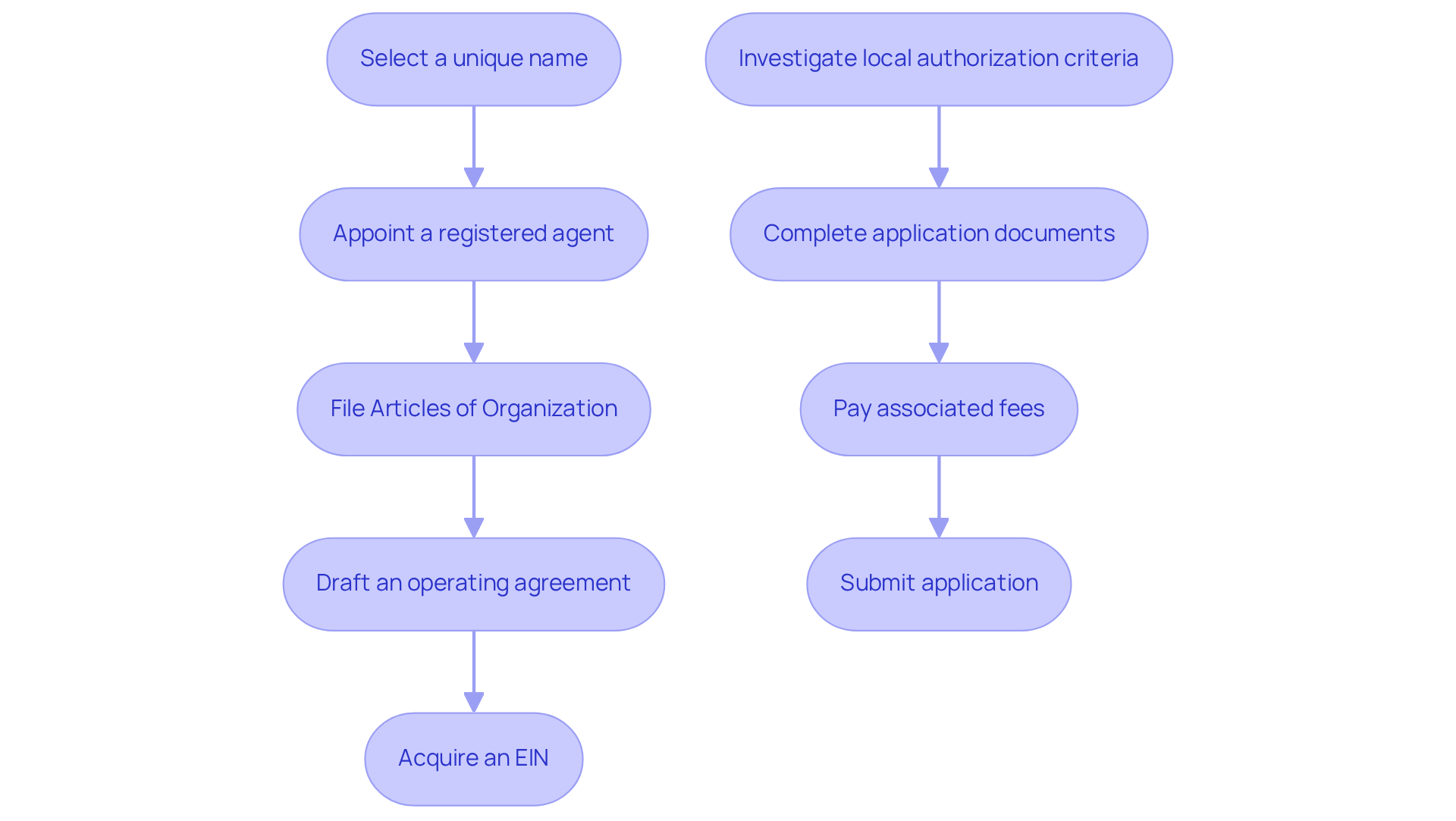
To establish a business license or LLC first, entrepreneurs typically follow these essential steps:
- Select a unique name that adheres to state regulations
- Appoint a registered agent
- File the Articles of Organization with the state
- Draft an operating agreement
- Acquire an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS
The procedure for acquiring a commercial permit generally involves:
- Investigating local authorization criteria specific to the type of enterprise and location
- Completing the required application documents
- Paying any associated fees
- Submitting the application to the appropriate governmental body
Accuracy in both processes is crucial to prevent delays and legal issues. For instance, in California, the approval for a Seller’s Permit can take several days to weeks, underscoring the importance of timely submissions. Additionally, understanding that some licenses require annual renewal can assist entrepreneurs in maintaining compliance and avoiding operational disruptions.
By adhering to these steps and remaining informed about local regulations, business owners can streamline their formation process and establish a solid foundation for their ventures.
Conclusion
Establishing a solid foundation for a new business requires critical decisions, particularly regarding the choice between a business license and an LLC. Each option serves distinct purposes: an LLC provides personal liability protection and a legal structure for the business, while a business license ensures compliance with local regulations. Understanding the nuances between these two options is essential for entrepreneurs seeking long-term success and effective risk management.
This article has explored the advantages and disadvantages of each choice. An LLC offers significant benefits, such as personal asset protection and tax flexibility, making it a favored option among startups. In contrast, while a business license is generally easier and quicker to obtain, it does not offer the liability protection that an LLC provides. Recognizing the specific requirements and processes for each is crucial, as neglecting these can result in costly penalties and operational setbacks.
Ultimately, entrepreneurs should approach the formation of their business with informed strategies. By prioritizing the establishment of an LLC or obtaining the necessary business licenses, they can enhance their credibility and navigate the complexities of regulatory compliance more effectively. This foundational knowledge not only safeguards personal interests but also lays the groundwork for sustainable business growth, underscoring the importance of making informed decisions throughout the entrepreneurial journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Limited Liability Company (LLC)?
A Limited Liability Company (LLC) is a legal entity that combines the benefits of corporations and partnerships, providing personal liability protection to its owners, which means personal assets are generally protected from company debts and lawsuits.
What is a business license?
A business license is an authorization granted by local government officials that allows a business to operate legally within a designated area, ensuring compliance with local regulations.
How do LLCs and business licenses differ?
An LLC establishes the legal framework for a business and provides liability protection, while a business license is necessary for compliance with local regulations and allows for the execution of specific commercial activities.
Why are LLCs becoming increasingly popular among businesses?
As of 2026, the number of businesses operating as LLCs is rising due to their flexibility and the liability protection they offer, making them a preferred choice for small and medium-sized enterprises.
What common mistake do startups make regarding LLCs and business licenses?
A common oversight among startups is assuming that obtaining a business license or forming an LLC is sufficient, often neglecting the need for additional permits required for specific operations, which can lead to penalties or operational disruptions.
Why is it important for entrepreneurs to understand the distinctions between LLCs and operating permits?
Understanding the differences between LLCs and operating permits is crucial for entrepreneurs to protect their investments and ensure compliance with regulations, helping to avoid costly errors, especially when expanding into new markets or regulated industries.