Introduction
The designation ‘Inc.’ holds considerable significance in the business realm, serving as a formal recognition of a company’s legal identity and its distinction from individual owners. This separation not only protects personal assets from corporate liabilities but also bolsters credibility among investors and customers.
As businesses confront the intricacies of incorporation, many find themselves questioning the true implications of adopting this status and how it stands in comparison to other business structures. Addressing these inquiries underscores the vital importance of comprehending ‘Inc.’ for anyone aspiring to establish a successful enterprise.
Define ‘Inc.’: Legal Meaning and Significance
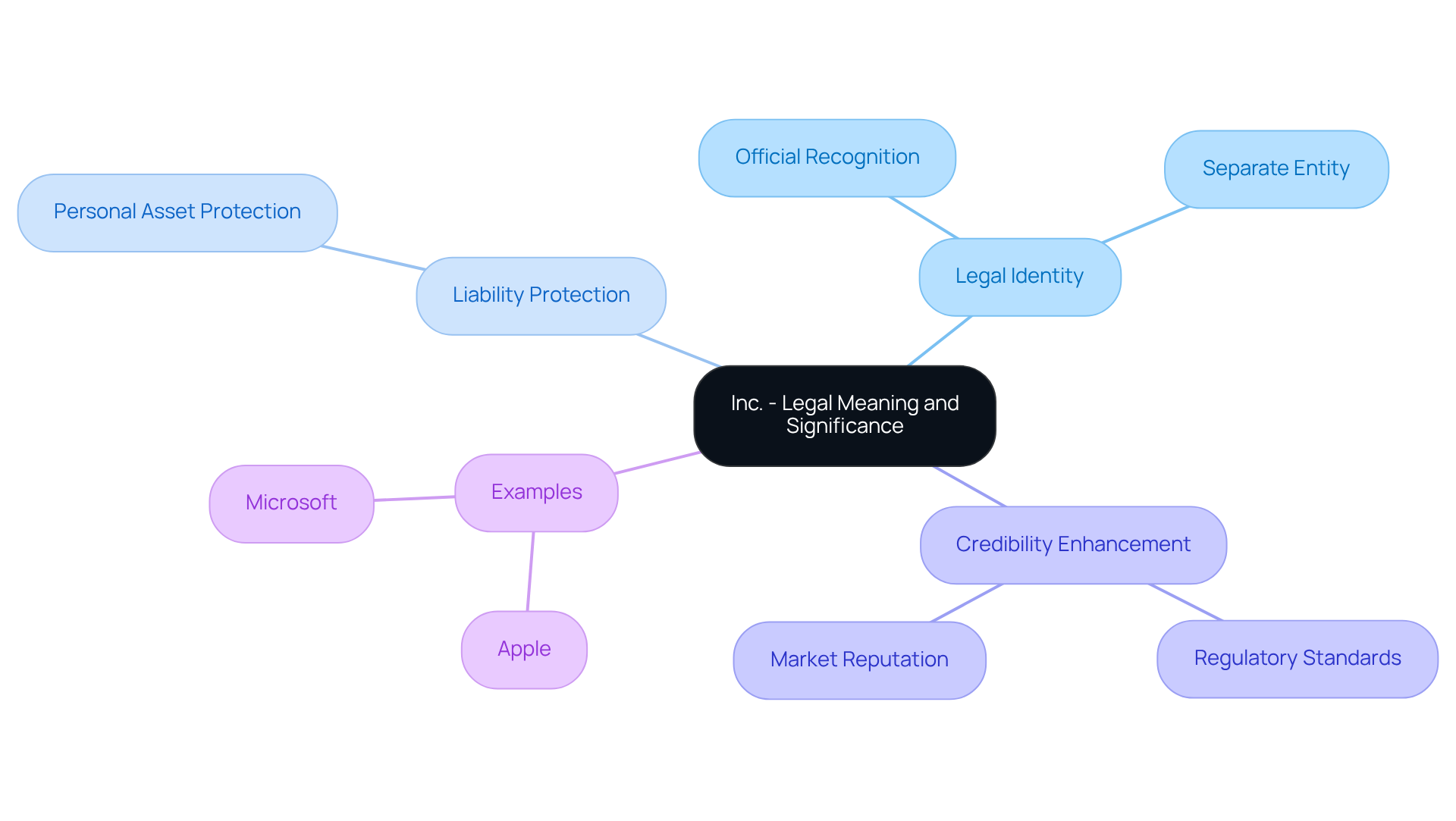
Inc.’ This signifies ‘incorporated,’ which is what que significa inc, indicating that a company has received official recognition as a legal entity through a formal incorporation process. This process involves submitting specific documents to the state government. The designation provides the enterprise with a distinct legal identity, separate from its owners, which is essential for limiting personal liability. As a result, shareholders are not personally liable for the corporation’s debts and obligations, thereby protecting their personal assets from potential claims against the company.
Moreover, the ‘Inc.’ designation enhances the company’s credibility, signaling to clients, investors, and partners that it adheres to regulatory standards and governance practices. For instance, companies like Apple and Microsoft have benefited from incorporation, not only by safeguarding their founders’ personal assets but also by enhancing their market reputation, which attracts investment and fosters trust among consumers. Experts emphasize that establishing an enterprise is a strategic move that mitigates risks while positioning the company for growth and sustainability in a competitive landscape.
Explore the Origin and Evolution of ‘Inc.’
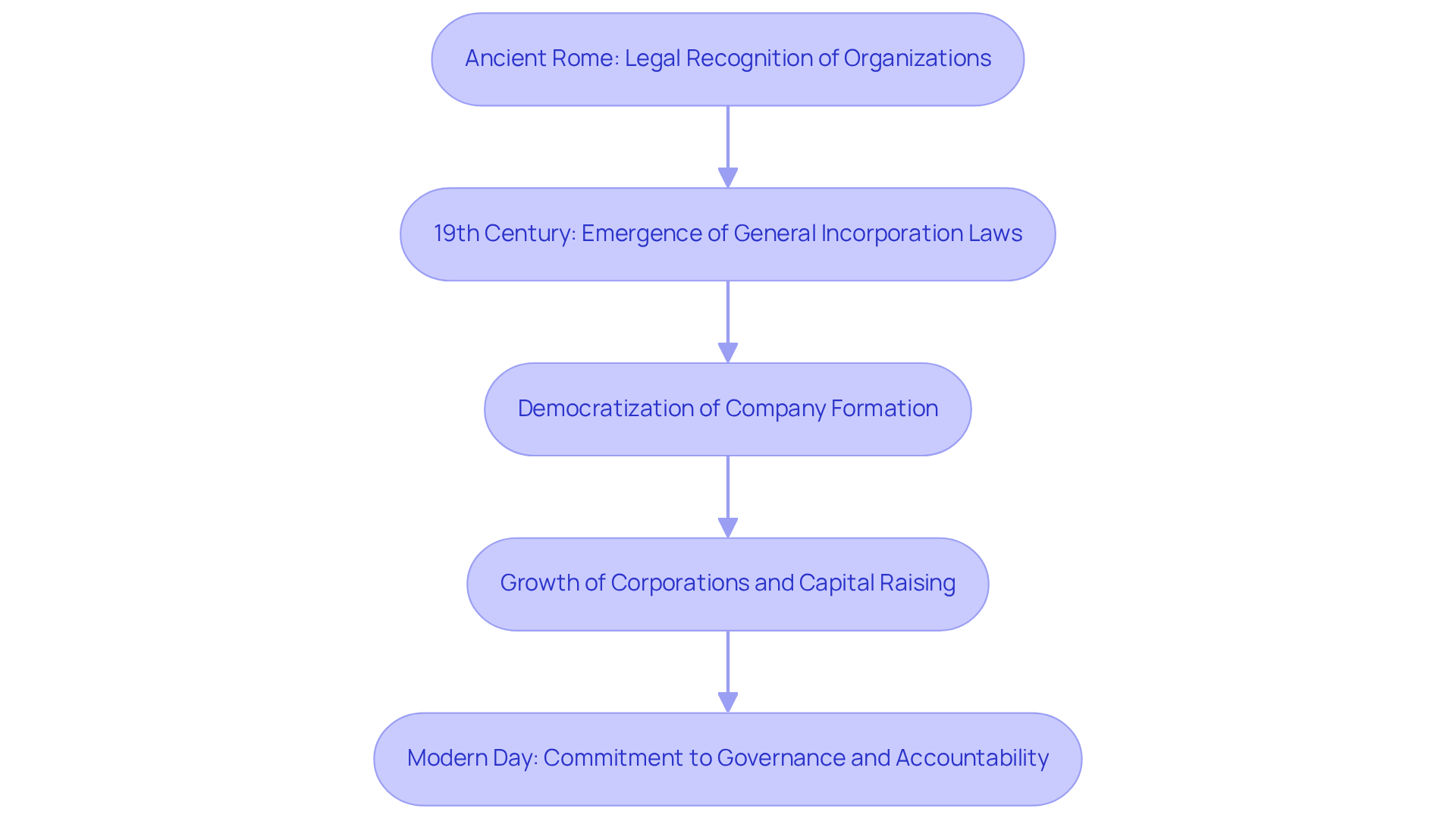
The concept of forming a legal entity has its roots in ancient Rome, where specific organizations received legal recognition to operate independently of their owners. In contrast, the modern notion of establishing a business entity began to emerge in the 19th century with the advent of general incorporation laws. These laws enabled businesses to form without requiring a special charter from the government, marking a significant shift in the landscape of corporate formation. This democratization of company formation not only facilitated the growth of corporations but also allowed them to raise capital more efficiently and operate under limited liability.
Over time, the regulatory framework governing incorporation has evolved, adapting to the complexities of contemporary commerce and the increasing demand for oversight. Today, the designation ‘Inc.’ signifies not merely a legal status but also a commitment to corporate governance and accountability, reflecting the expectations of stakeholders in a modern business environment.
Identify Key Characteristics and Legal Implications of ‘Inc.’
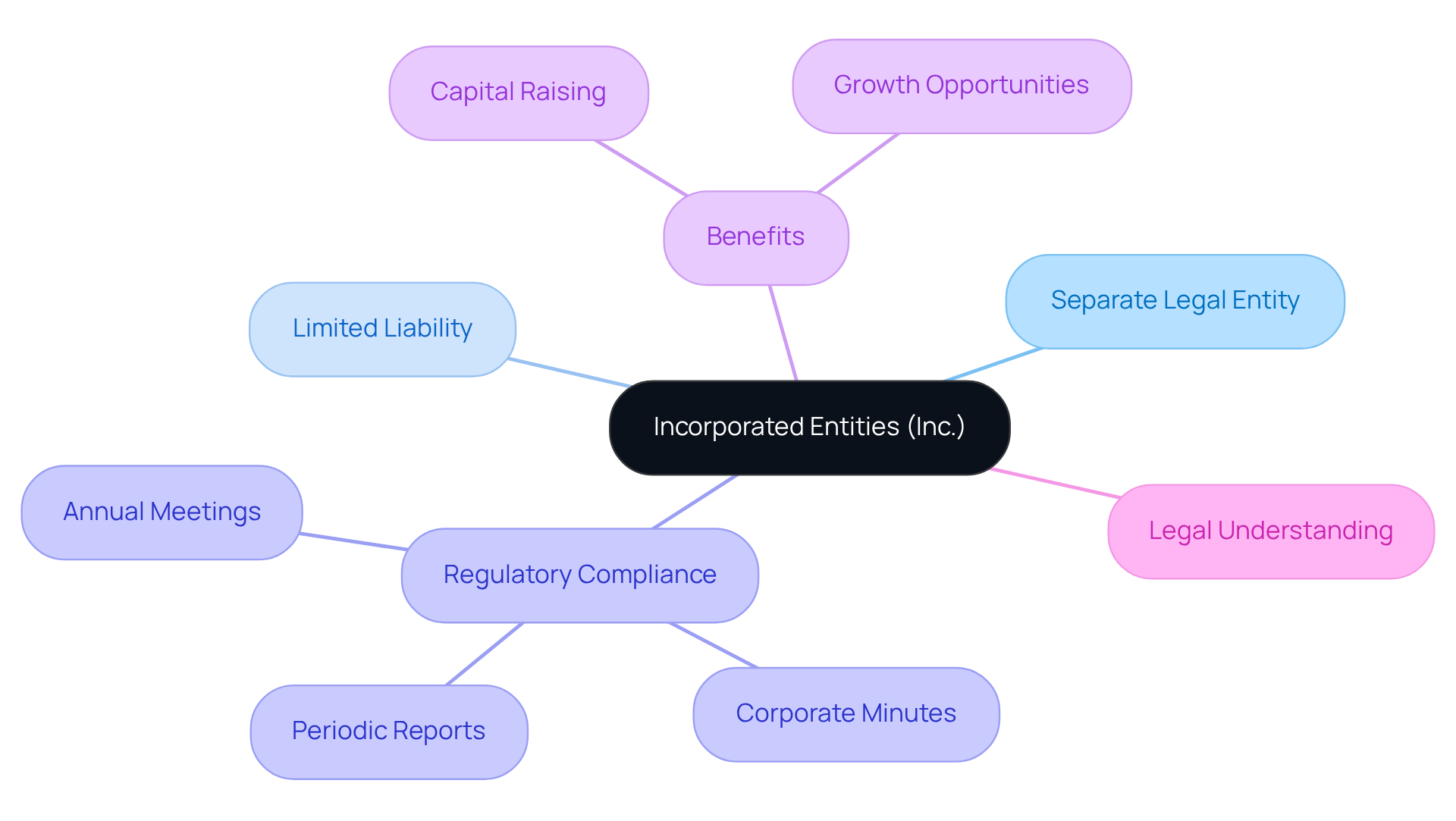
Incorporated entities, designated by the term ‘Inc.’, exhibit distinct characteristics that differentiate them from other business structures. Primarily, they operate as separate legal entities, allowing them to enter contracts, sue, and be sued independently of their owners. This separation provides limited liability protection, meaning shareholders are only responsible for the entity’s debts up to their investment amount.
Moreover, companies must comply with specific regulatory requirements, including:
- Conducting annual meetings
- Maintaining corporate minutes
- Filing periodic reports with state authorities
Adhering to these obligations is crucial, as failure to comply can result in penalties or even administrative dissolution, particularly in light of recent legislative changes across various states.
Additionally, corporations benefit from the ability to raise capital through stock sales, significantly enhancing growth opportunities. However, this structure also invites increased scrutiny and necessitates a thorough understanding of corporate governance. Therefore, it is essential for owners to remain informed about evolving legal standards and compliance requirements.
Differentiate ‘Inc.’ from Other Business Structures
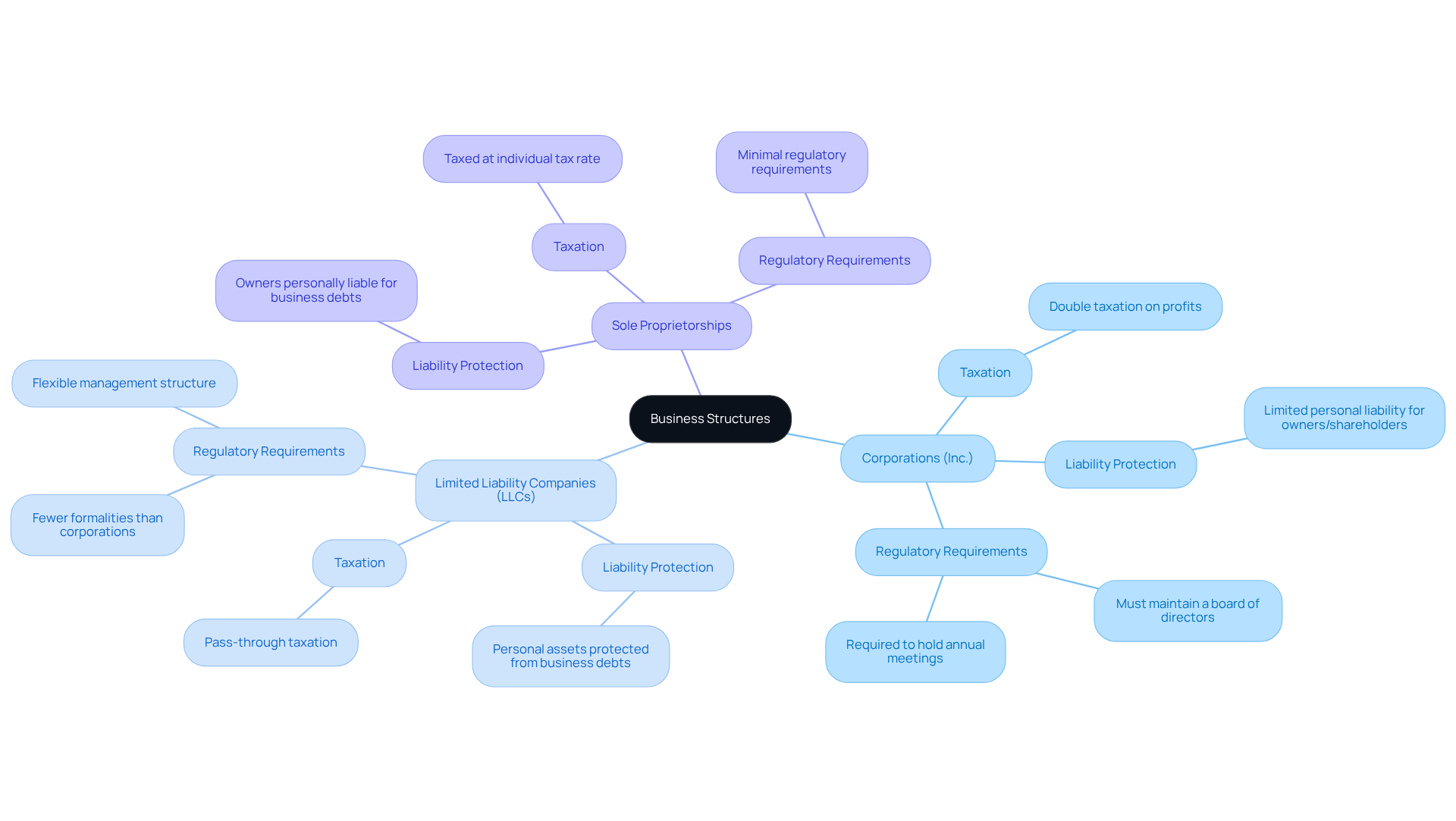
When comparing ‘Inc.’, it is important to understand what que significa inc to other organizational structures such as Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) and sole proprietorships, several key differences emerge. Corporations offer robust personal liability protection for their owners, effectively shielding them from business debts. In contrast, sole proprietorships expose owners to personal liability, which can be a significant risk.
LLCs also provide limited liability protection but are generally more flexible in terms of management and taxation. While corporations must adhere to stricter regulatory requirements – including maintaining a board of directors and conducting formal meetings – LLCs benefit from fewer formalities. This flexibility allows LLC owners to concentrate on growth and operational efficiency.
Moreover, corporations may encounter double taxation on profits – first at the corporate level and again when dividends are distributed to shareholders. Conversely, LLCs typically enjoy pass-through taxation, meaning profits are taxed only at the individual member level. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for entrepreneurs navigating the complexities of business formation and selecting the structure that aligns with their long-term objectives.
For international entrepreneurs, establishing a company in states like Wyoming, Florida, and Delaware can offer strategic advantages. Wyoming is recognized for its business-friendly environment, making it an appealing choice for new ventures. Florida’s favorable tax policies can support startups in thriving, while Delaware is celebrated for its advantageous corporate laws, attracting many businesses. However, it is essential to consider the challenges faced by LLCs, such as compliance confusion and multi-state complications, which can affect their operational efficiency.
Conclusion
The designation ‘Inc.’ carries significant weight for businesses, symbolizing not only a legal status but also a commitment to operational integrity and accountability. By incorporating, companies establish themselves as distinct legal entities, which protects owners from personal liability and bolsters their credibility in the marketplace. This crucial step in business formation is essential for fostering growth and sustainability in an increasingly competitive environment.
Key points discussed throughout the article include:
- The historical evolution of incorporation
- The unique characteristics of ‘Inc.’ entities
- Their distinctions from other business structures such as LLCs and sole proprietorships
The legal implications of incorporation, including limited liability protection and compliance requirements, highlight the necessity of understanding this designation. Additionally, the advantages of incorporation – ranging from enhanced fundraising capabilities to increased market trust – are vital considerations for entrepreneurs evaluating their business structure.
Incorporating a business as ‘Inc.’ transcends mere procedural steps; it represents a strategic decision that can profoundly influence long-term success. For entrepreneurs and business owners, grasping the full implications of this designation can lead to more informed choices that align with their objectives. As the landscape of corporate governance continues to evolve, staying informed about the legal and operational nuances of incorporation will equip businesses to navigate challenges and seize opportunities in their respective markets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does ‘Inc.’ stand for?
‘Inc.’ stands for ‘incorporated,’ indicating that a company has been officially recognized as a legal entity through a formal incorporation process.
What is the incorporation process?
The incorporation process involves submitting specific documents to the state government to establish a company as a separate legal entity.
What are the legal benefits of incorporating a company?
Incorporating a company provides it with a distinct legal identity separate from its owners, which limits personal liability for shareholders regarding the corporation’s debts and obligations.
How does incorporation protect shareholders?
Shareholders are not personally liable for the corporation’s debts and obligations, which protects their personal assets from potential claims against the company.
How does the ‘Inc.’ designation affect a company’s credibility?
The ‘Inc.’ designation enhances a company’s credibility by signaling to clients, investors, and partners that it adheres to regulatory standards and governance practices.
Can you provide examples of companies that have benefited from incorporation?
Companies like Apple and Microsoft have benefited from incorporation by safeguarding their founders’ personal assets and enhancing their market reputation.
What strategic advantages does incorporation provide for a business?
Incorporation mitigates risks and positions the company for growth and sustainability in a competitive landscape.