Introduction
Forming an incorporated company in the U.S. presents a complex challenge, particularly for aspiring entrepreneurs. It is essential to understand the legal frameworks, select the appropriate business structure, and ensure compliance with various regulations. These steps are critical in navigating this intricate process. This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap, outlining key considerations and practical steps that can empower individuals to successfully establish their enterprises. In a competitive landscape, identifying the key factors that could influence the success or failure of a new business venture is paramount.
Understand the Basics of Company Formation in the U.S.
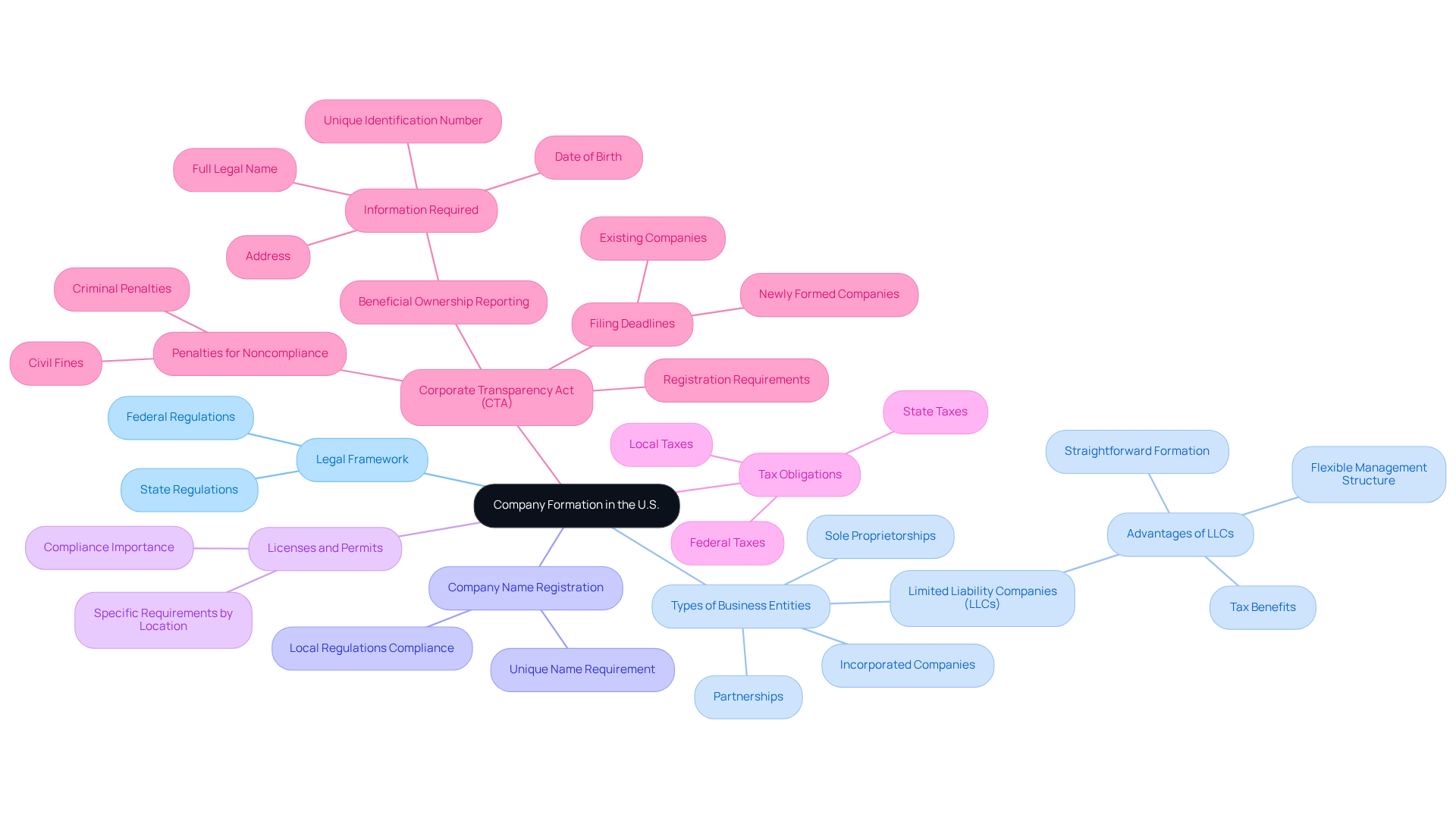
Before starting an enterprise in the U.S., it is essential to understand the foundational elements of an incorporated company. This encompasses legal requirements, the various types of incorporated companies, and the implications of each option. Key considerations include:
- Legal Framework: Familiarize yourself with both federal and local regulations governing commercial activities. Each state has distinct regulations, making it crucial to research the specific requirements for your intended location.
- Types of Business Entities: Recognize the different organizational forms available, such as incorporated companies, sole proprietorships, partnerships, and limited liability companies (LLCs). LLCs offer advantages due to their straightforward formation, flexible management structure, and tax benefits, while an incorporated company may be more suitable for larger-scale initiatives and investments. Consulting with experts, such as the team at Social Enterprises, can assist in selecting the appropriate structure for your gaming or e-commerce venture.
- Company Name Registration: Verify that your chosen company name is unique and adheres to local regulations. This typically involves checking with the regional commercial registry to avoid conflicts.
- Licenses and Permits: Depending on your enterprise type and location, specific licenses or permits may be required for legal operation. Ensure compliance to mitigate potential legal issues.
- Tax Obligations: Grasp the tax responsibilities linked to your chosen enterprise structure, including federal, state, and local taxes. This understanding is vital for maintaining compliance and avoiding penalties. Engaging with Social Enterprises can clarify federal tax returns and other obligations that may arise.
- Corporate Transparency Act (CTA): Starting January 1, 2024, most small enterprises must register with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) under the CTA. This includes reporting beneficial ownership information, which is critical for compliance. Businesses must keep their registration current and report any changes within 30 days to avoid penalties, which may include civil fines and criminal repercussions for non-compliance.
By mastering these fundamentals, you will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of launching a venture in the U.S., ensuring a smoother entry into the market.
Choose the Right Business Structure: LLC vs. Corporation
Choosing the appropriate organizational framework is crucial for your company’s success. This section outlines the two most prevalent structures:
-
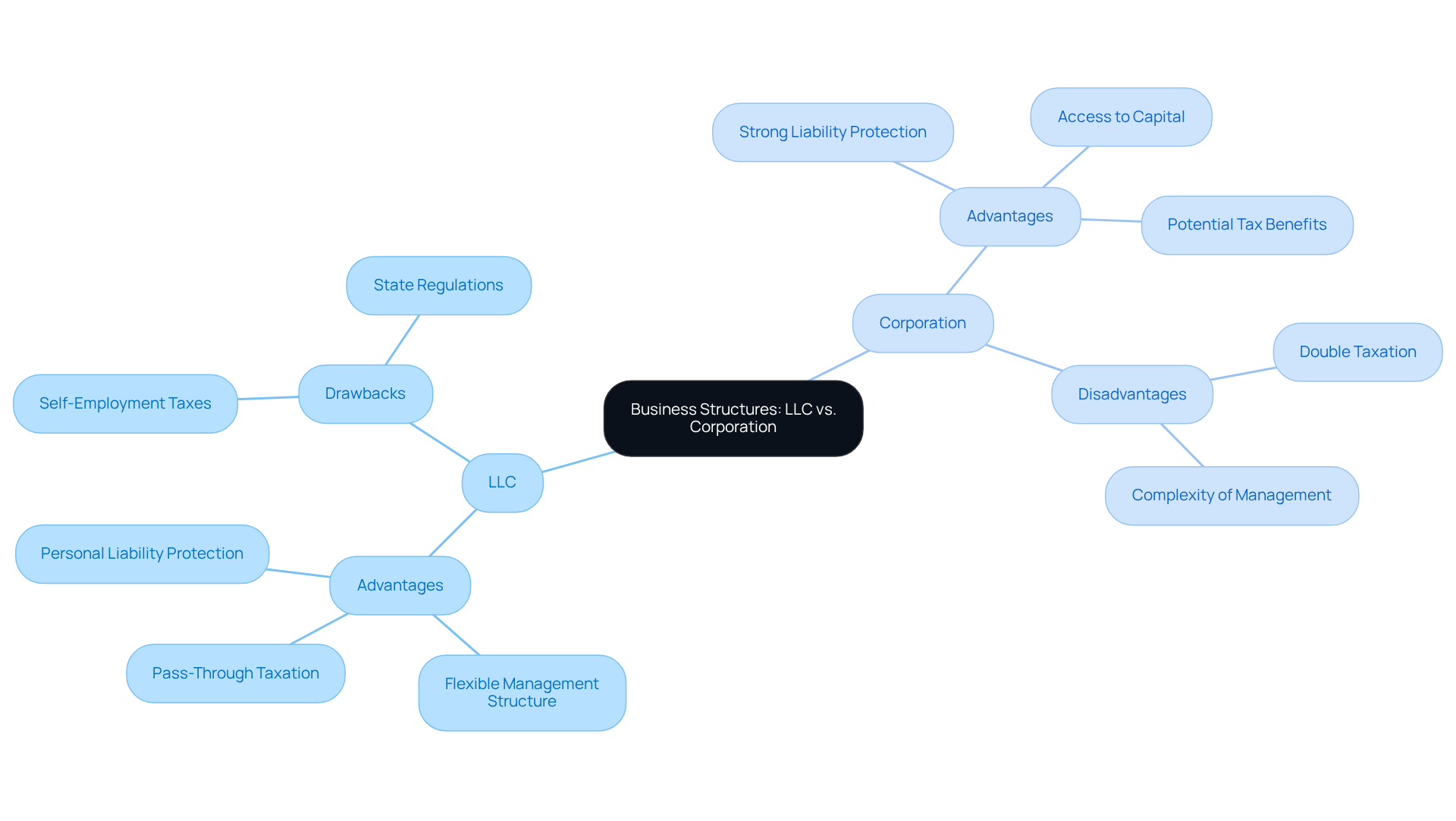
Limited Liability Company (LLC):
- Advantages: LLCs offer personal liability protection, enabling owners to separate personal assets from business liabilities. They also provide flexible management structures and pass-through taxation, which allows profits to be taxed at the owner’s personal tax rate, thus avoiding double taxation. In 2026, LLCs have gained popularity, with a significant increase in formations driven by entrepreneurs seeking legal protection while pursuing multiple ventures. For e-commerce businesses, LLCs can deliver beneficial tax advantages and streamlined compliance processes, particularly in states like Delaware and Wyoming.
- Drawbacks: Despite their many benefits, LLCs may be subject to self-employment taxes, and regulations can vary significantly by state, complicating compliance for remote founders.
-
Corporation:
- Advantages: Corporations provide strong liability protection and facilitate easier access to capital through stock sales. They may also offer potential tax benefits, especially for businesses with substantial profits. However, the complexity of managing a corporation and the need to comply with more regulations can be overwhelming for new entrepreneurs, particularly those from international backgrounds.
- Disadvantages: Corporations face double taxation, where both the corporation and its owners are taxed on profits, which can be a considerable disadvantage for small business owners.
When deciding between an LLC and a corporation, it is essential to consider key factors such as your objectives, acceptable risk levels, and financial circumstances. For example, many startups in 2026 are choosing LLCs due to their flexibility and lower compliance burdens, while others may prefer corporations to attract investors. Consulting with a tax advisor can provide tailored guidance based on your specific situation, ensuring that your organizational framework aligns with your long-term goals. As experts indicate, “Selecting the appropriate organizational framework is one of the most critical legal decisions you will make when launching a business.
Register Your Business: Step-by-Step Registration Process
Registering your enterprise involves several essential steps to ensure a smooth process. Follow this guide to navigate the registration effectively:
-
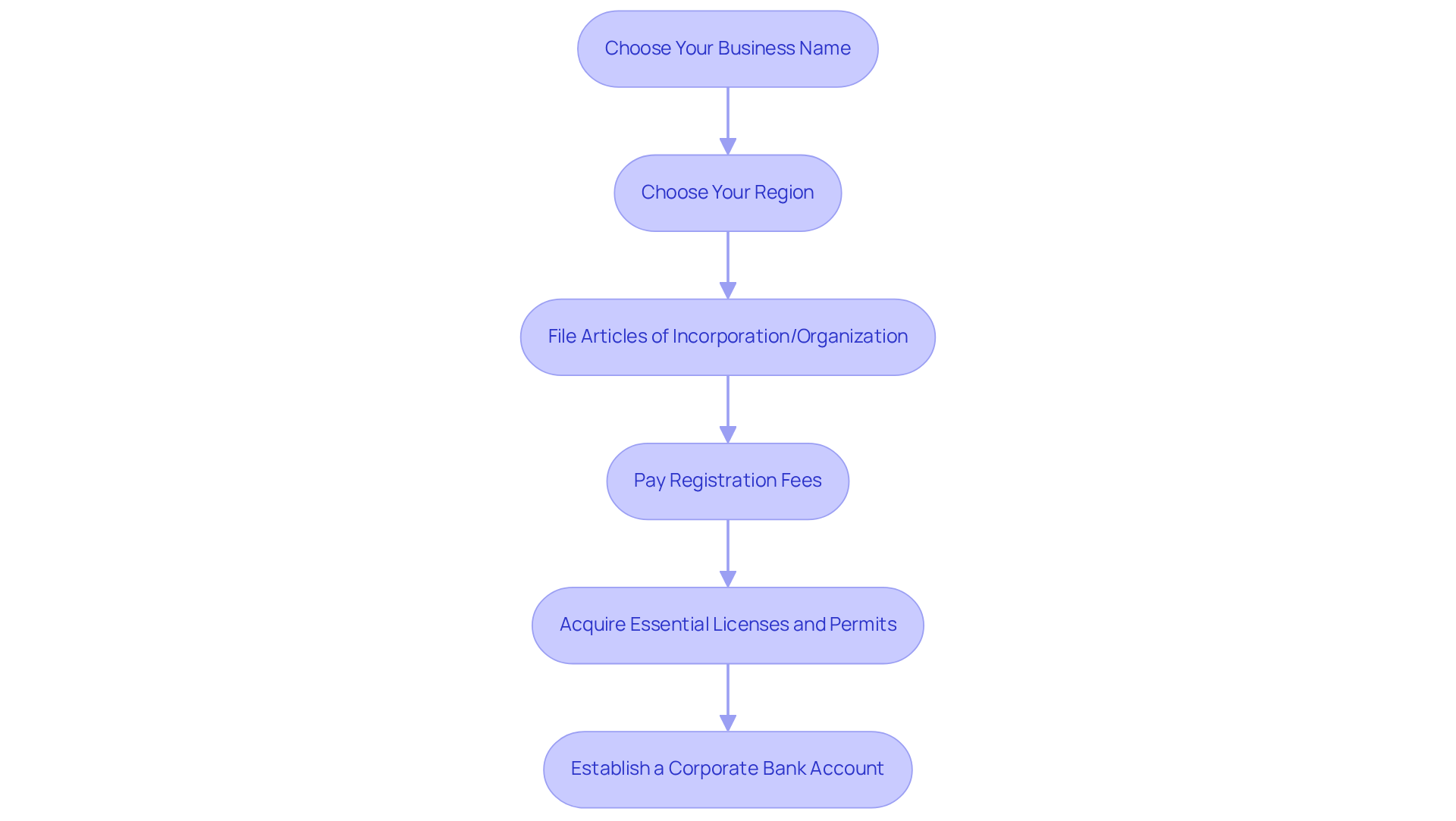
Choose Your Business Name: Selecting a distinctive name is crucial, as it must comply with local naming regulations. A unique name not only aids in brand recognition but also mitigates potential legal issues. Verify availability through your region’s company registry to confirm that your chosen name is not already in use.
-
Choose Your Region: Determine where to register your enterprise, typically in the area where you will conduct most of your activities. Each region has its own regulations and advantages, so consider factors such as tax implications and the economic environment.
-
File Articles of Incorporation/Organization: Prepare and submit the necessary documents to your region’s Secretary of State office. This includes information about your enterprise structure, purpose, and registered agent. For instance, New York saw a significant increase in enterprise applications, reaching 313,481 in 2023, highlighting the region’s vibrant entrepreneurial landscape.
-
Pay Registration Fees: Be ready to cover any required fees associated with the registration process, which can vary by region. For example, the standard registration fee for corporations is approximately $500, while other types of enterprises may incur fees around $200. Understanding these costs upfront can facilitate effective budgeting.
-
Acquire Essential Licenses and Permits: Research and apply for any local, state, or federal licenses necessary for your enterprise type. This step is vital to ensure compliance with regulations and to avoid penalties.
-
Establish a Corporate Bank Account: Open a separate bank account for your enterprise to maintain a clear distinction between personal and business finances. This practice simplifies accounting and enhances your organization’s credibility.
By following these steps, you will successfully register your enterprise and lay a solid foundation for its operations. Recent updates indicate that states are continually improving their registration procedures, making it essential to stay informed about any changes that may affect your company setup.
Ensure Compliance: Obtain EIN and ITIN Numbers
To operate legally and efficiently in the U.S., obtaining the appropriate tax identification numbers is essential:
-
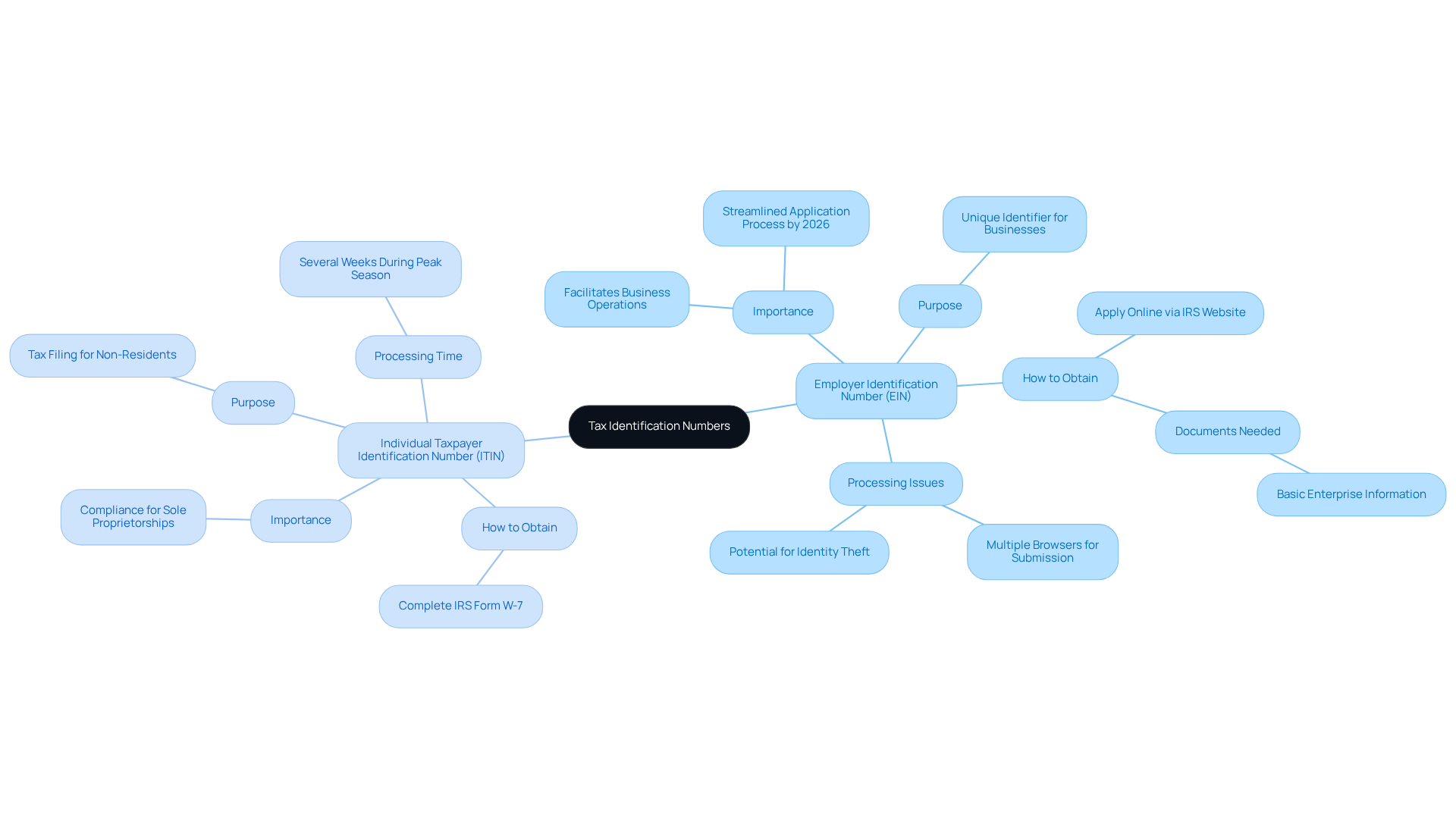
Employer Identification Number (EIN):
- Purpose: An EIN is crucial for businesses with employees, partnerships, and corporations, serving as a unique identifier for tax reporting and compliance. It functions similarly to a Social Security number but is specifically designated for enterprises.
- Importance: The IRS aims to streamline the EIN application process by 2026, enhancing accessibility and efficiency. Quick access to an EIN allows entrepreneurs to focus on developing their ventures rather than navigating bureaucratic hurdles.
- How to Obtain: Apply online through the IRS website, where the process can be completed in minutes. Successful applicants can download the CP 575 notice confirming their EIN immediately. If issues arise during submission, it is advisable to try multiple web browsers.
- Documents Needed: Basic information about your enterprise, including its structure and ownership.
-
Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN):
- Purpose: An ITIN is necessary for individuals who need to file taxes but do not qualify for a Social Security number, often utilized by non-resident aliens.
- Importance: Businesses requiring an ITIN for tax purposes include sole proprietorships and partnerships that do not have employees but still need to comply with tax regulations.
- How to Obtain: Complete IRS Form W-7 and submit it along with your tax return or other required documentation.
- Processing Time: Allow several weeks for processing, especially during peak tax season, as the IRS prioritizes EIN applications to reduce backlogs. Some applicants have reported receiving EINs they did not request, raising concerns about errors or identity theft.
By securing these identification numbers, you ensure adherence to federal tax regulations, facilitating smoother operations and enhancing your ability to establish a successful presence in the U.S.
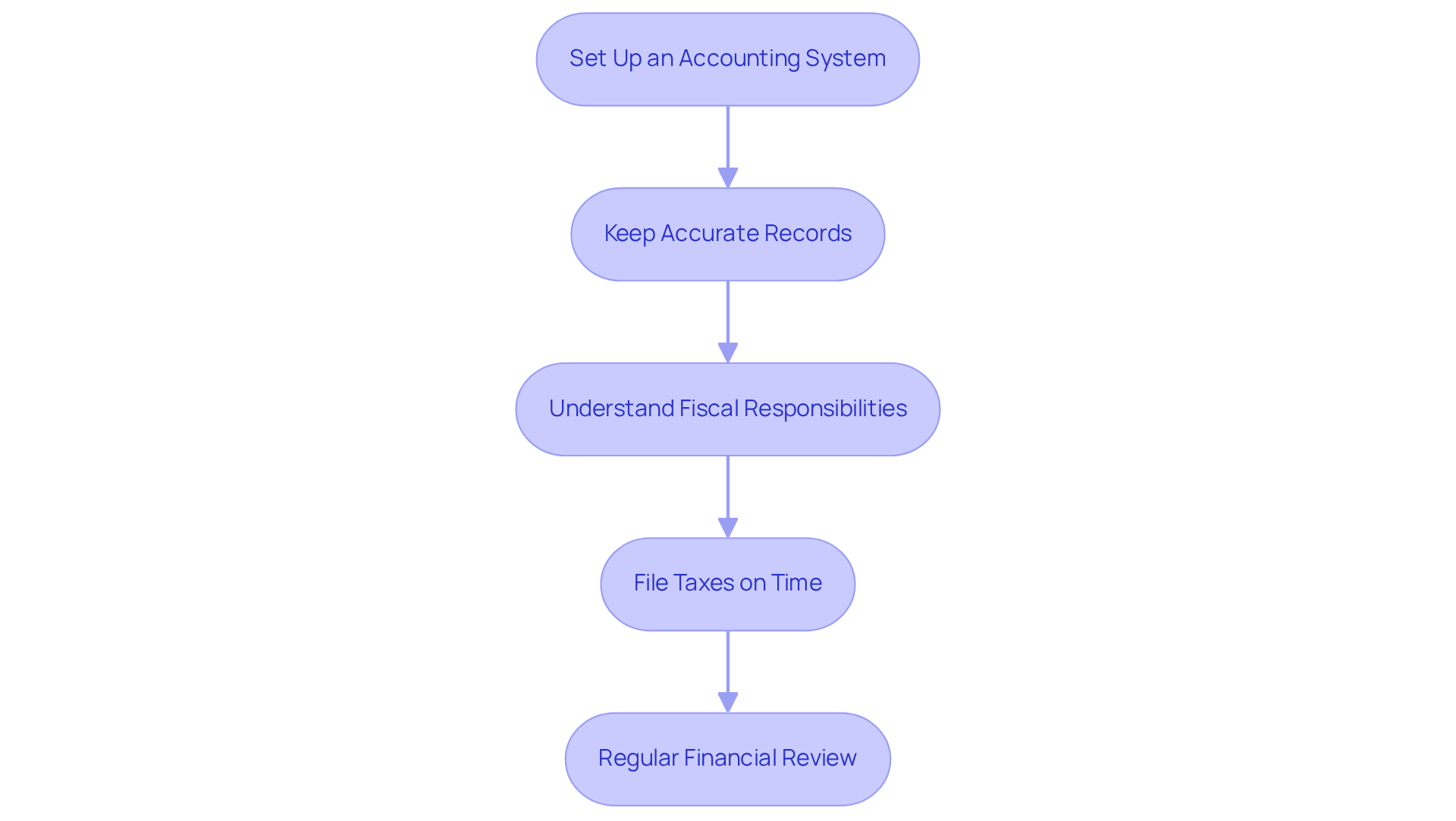
Manage Your Business: Accounting and Tax Filing Essentials
Effective management of business finances is essential for long-term success. Implementing the following accounting and tax filing practices can significantly enhance your financial health:
-
Set Up an Accounting System: Decide between cash or accrual accounting methods and establish a robust system to track income and expenses. Utilizing accounting software can greatly improve efficiency and accuracy in financial reporting.
-
Keep Accurate Records: It is vital to maintain detailed records of all financial transactions, including receipts, invoices, and bank statements. Inaccurate or missing documentation can result in missed deductions and IRS penalties, making meticulous record-keeping crucial for tax filing and financial analysis.
-
Understand Fiscal Responsibilities: Familiarize yourself with federal, regional, and local financial requirements, including income taxes, sales taxes, and payroll contributions if you employ staff. The United States operates under a progressive tax system, meaning individuals with higher taxable incomes pay higher federal income taxes. Additionally, while most states impose a sales tax, five states – Delaware, Alaska, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon – are exempt from sales tax. Staying informed about the latest tax filing requirements is essential for compliance for an incorporated company in the U.S.
-
File Taxes on Time: Meeting all tax filing deadlines is imperative to avoid penalties. Engaging a tax expert can be beneficial, particularly for complex submissions, ensuring that your enterprise adheres to all regulations.
-
Regular Financial Review: Conducting regular reviews of your financial statements enables you to assess your organization’s performance and make informed decisions. Research indicates that businesses with organized financial records are more likely to succeed, as they can swiftly adapt to changing market conditions.
By implementing these practices, you will not only maintain compliance but also ensure the financial health of your business, positioning it for sustainable growth.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of forming an incorporated company in the U.S. is crucial for aspiring entrepreneurs. This guide has outlined the essential steps involved, from grasping the foundational elements of company formation to navigating the registration process and ensuring ongoing compliance. By familiarizing themselves with the legal requirements and the various business structures available, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their objectives.
Key insights highlight the importance of selecting the appropriate business structure, whether it be an LLC or a corporation, and the implications of each choice on liability, taxation, and operational flexibility. Additionally, the step-by-step registration process, which includes obtaining necessary identification numbers and licenses, establishes the groundwork for a successful business launch. Effective financial management practices, such as implementing accounting systems and ensuring timely tax filings, are vital for sustaining growth and compliance.
Ultimately, forming an incorporated company in the U.S. transcends merely meeting legal requirements; it is about laying a solid foundation for future success. Entrepreneurs are encouraged to seek expert guidance and remain informed about evolving regulations to navigate this complex landscape with confidence. Taking proactive steps today can pave the way for a thriving enterprise tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the foundational elements of company formation in the U.S.?
The foundational elements include understanding legal requirements, types of business entities, company name registration, licenses and permits, tax obligations, and compliance with the Corporate Transparency Act (CTA).
What legal framework should I be aware of when starting a business in the U.S.?
It is essential to familiarize yourself with both federal and local regulations, as each state has distinct regulations that govern commercial activities.
What types of business entities are available for incorporation?
The main types include incorporated companies, sole proprietorships, partnerships, and limited liability companies (LLCs). LLCs are popular for their straightforward formation and tax benefits.
Why might I choose an LLC over a corporation?
LLCs offer personal liability protection, flexible management structures, and pass-through taxation, avoiding double taxation. They are particularly beneficial for e-commerce businesses.
What are the potential drawbacks of forming an LLC?
LLCs may be subject to self-employment taxes, and regulations can vary significantly by state, complicating compliance for remote founders.
What advantages do corporations provide?
Corporations offer strong liability protection and easier access to capital through stock sales, along with potential tax benefits for profitable businesses.
What disadvantages should I consider when forming a corporation?
Corporations face double taxation, where both the corporation and its owners are taxed on profits, which can be a significant drawback for small business owners.
How can I ensure my chosen company name is compliant?
You should verify that your chosen company name is unique and adheres to local regulations by checking with the regional commercial registry.
What licenses or permits might I need to operate legally?
Depending on your business type and location, specific licenses or permits may be required to ensure legal operation.
What are the tax obligations associated with different business structures?
It is important to understand the federal, state, and local tax responsibilities linked to your chosen structure to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
What is the Corporate Transparency Act (CTA)?
Starting January 1, 2024, most small enterprises must register with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) and report beneficial ownership information to comply with the CTA.
How can I determine the best business structure for my needs?
Consider key factors such as your objectives, acceptable risk levels, and financial circumstances. Consulting with a tax advisor can provide tailored guidance to align your structure with your long-term goals.