Introduction
Understanding the nuances of tax identification is essential for businesses, especially in a landscape where compliance is critical. The distinction between an Employer Identification Number (EIN) and a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is not merely academic; it has significant implications for operational efficiency and regulatory adherence. As organizations navigate their tax obligations, a pressing question arises: Are EIN and TIN truly interchangeable, or do they serve distinct purposes that can impact business operations? Exploring these differences is vital for anyone aiming to ensure compliance and optimize their tax strategy.
Define EIN and TIN: Key Concepts
An Employer Identification Number (EIN) is a unique nine-digit code assigned by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for tax purposes, commonly known as a Federal Tax Number. EINs play a vital role in various business operations, including:
- Hiring employees
- Opening bank accounts
- Obtaining credit
- Filing taxes, particularly for e-commerce and gaming enterprises in the U.S.
In contrast, a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is a broader term that includes various identification numbers used by the IRS, such as EINs, and this leads to the question, are EIN and TIN the same? Understanding these definitions is crucial for navigating the complexities of tax identification. Businesses in the United States, especially those in the e-commerce and gaming sectors, must obtain a TIN to comply with tax regulations.
Without a TIN, individuals cannot file taxes or meet IRS requirements, which may result in penalties. This underscores the importance of these identifiers in ensuring accurate tax reporting and compliance, particularly for entities that need to hire employees, open bank accounts, or file tax returns.
Differentiate Between EIN and TIN: Key Differences
The primary distinction between an Employer Identification Number (EIN) and a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is rooted in their specific applications and scope. An EIN is exclusively assigned to commercial entities for tax reporting and compliance, while TIN serves as a broader term encompassing various taxpayer identification numbers, including those for individuals. Notably, all EINs qualify as TINs; however, when considering whether EIN and TIN are the same, it is important to note that not all TINs are EINs. Individuals typically utilize their Social Security Numbers (SSNs) as TINs, whereas organizations, particularly those with employees, are required to obtain an EIN to fulfill their tax obligations.
This differentiation is crucial for ensuring compliance with IRS regulations and facilitating effective tax reporting. Statistics indicate that organizations with employees must secure an EIN to manage payroll taxes and submit employment tax returns, underscoring the significance of understanding these identifiers for operational success. Furthermore, a range of enterprises, from corporations to partnerships, depend on EINs for tax compliance, while sole proprietorships may utilize their SSNs, contingent upon state regulations. Understanding these distinctions is essential for navigating the complexities of commercial operations and maintaining regulatory compliance.
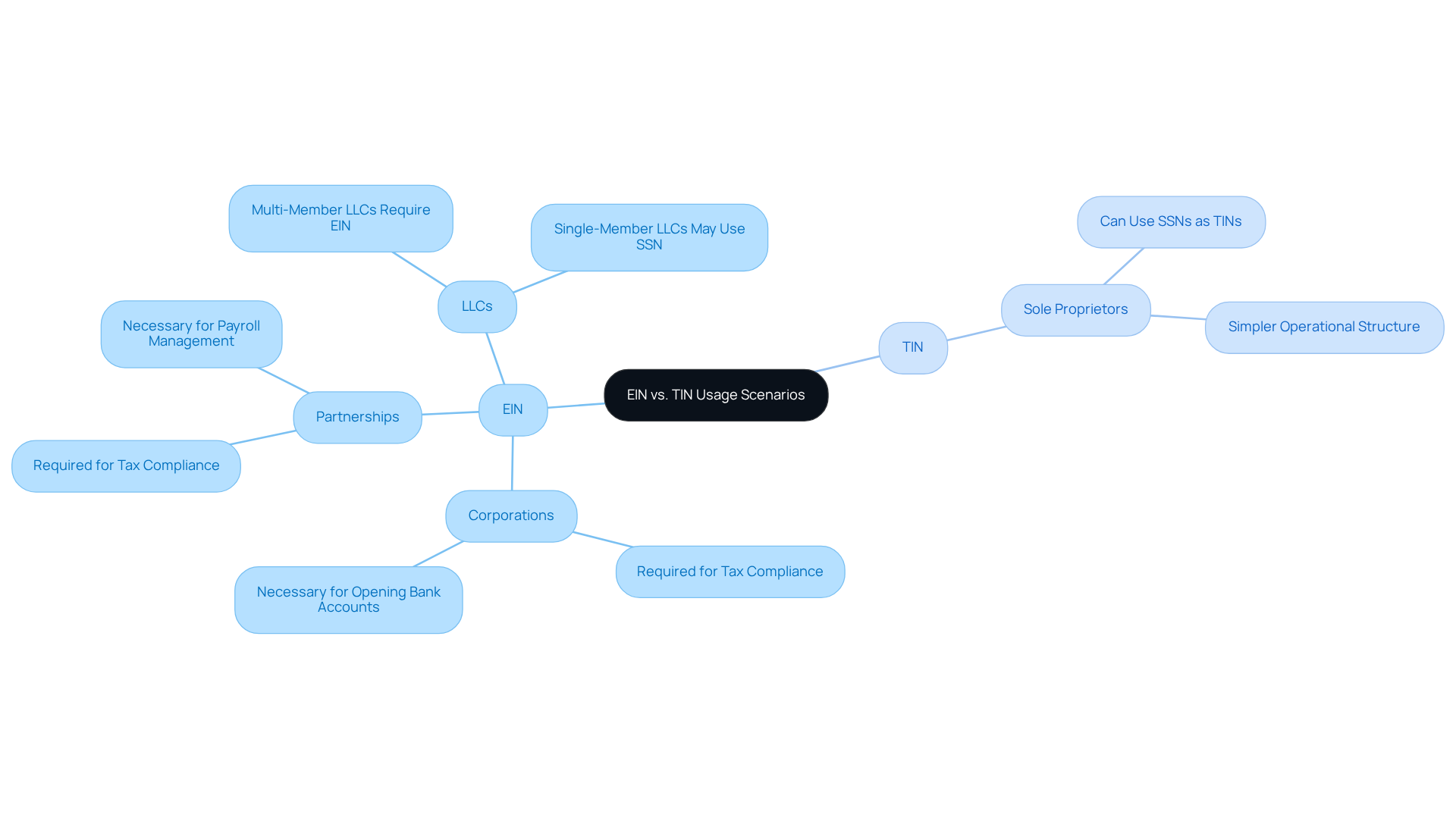
Understand Usage Scenarios: When to Use EIN vs. TIN
EINs are essential for entities that employ staff, operate as corporations or partnerships, or need to file specific tax returns. For instance, when establishing a new LLC or corporation, obtaining an EIN is vital for opening a company bank account and fulfilling tax obligations. Conversely, sole proprietors without employees can use their Social Security Numbers (SSNs) as their Tax Identification Numbers (TINs), leading to the question of whether EIN and TIN are the same. Recent data indicates that a considerable number of sole proprietors in the U.S. prefer SSNs over EINs, reflecting their simpler operational structure.
Understanding these distinctions is critical for ensuring compliance with tax regulations and for addressing whether EIN and TIN are the same based on your business model. For example, startups organized as LLCs with multiple members must apply for an EIN, while single-member LLCs may not require one unless they choose to hire employees or change their structure. This clarity aids entrepreneurs in effectively navigating the complexities of U.S. tax requirements.
Apply for EIN and TIN: Step-by-Step Process
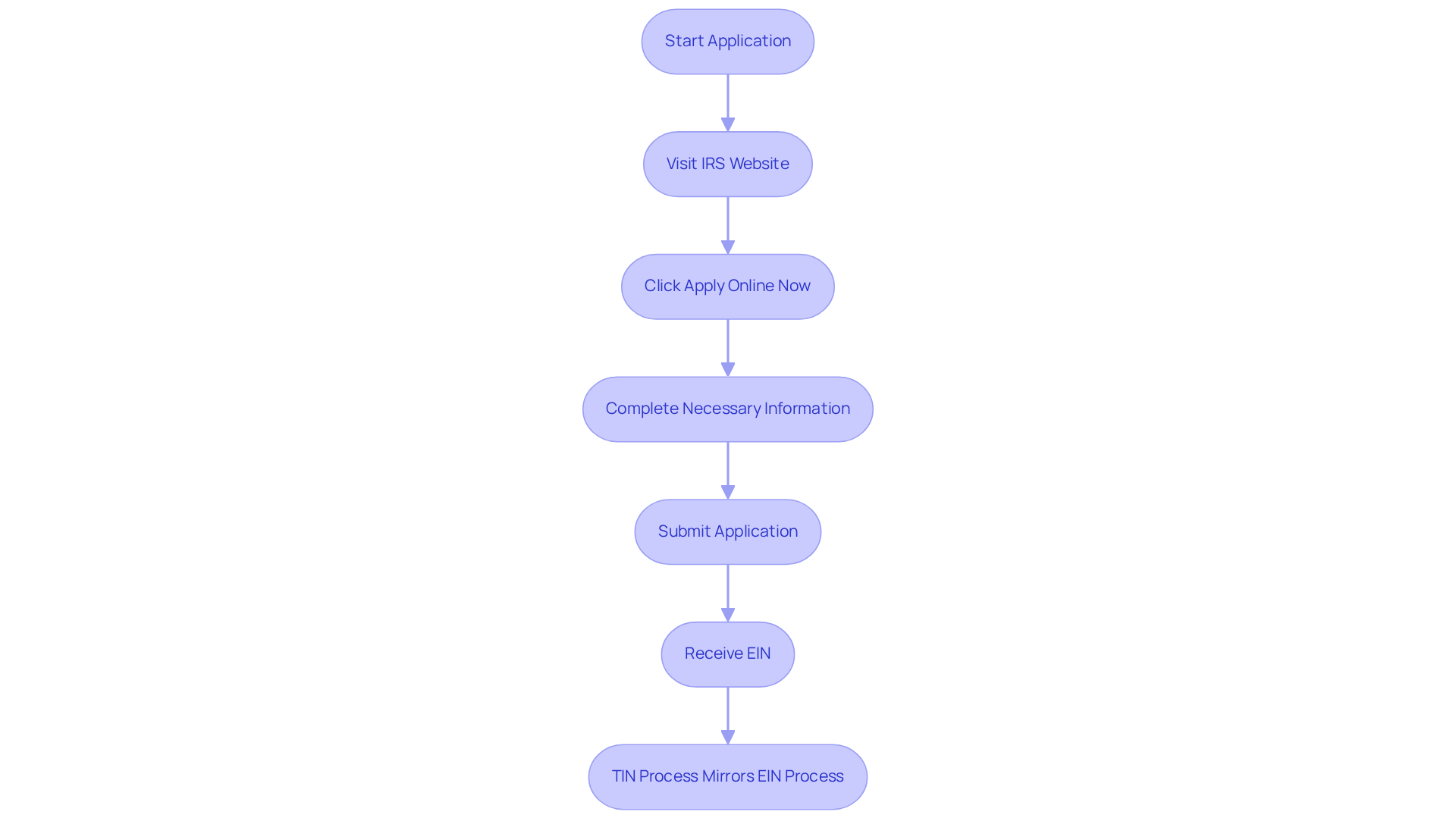
To apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN), follow these steps:
- Visit the IRS website and navigate to the EIN application section.
- Click on ‘Apply Online Now’ and select your enterprise structure.
- Complete the necessary information, including your company name, address, and the name of the responsible party.
- Submit the application.
You will receive your EIN immediately upon approval, making the online application the fastest method available. As of 2026, the IRS continues to streamline this process, encouraging electronic submissions to enhance efficiency.
For a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN), individuals needing an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) should complete Form W-7 and submit it along with their tax return. If applying for a TIN as an enterprise, the process typically mirrors that of obtaining an EIN, leading to the question of whether EIN and TIN are the same. It is essential to have all necessary documentation ready, as this will facilitate a smooth application process. Statistics indicate that a significant number of EIN applications are submitted online, reflecting a growing preference for digital applications over paper submissions, which can take longer to process. Successful examples of international businesses obtaining their EINs underscore the effectiveness of diligently following these steps.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between an Employer Identification Number (EIN) and a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is crucial for businesses navigating tax compliance and operational efficiency. While both identifiers are essential for fulfilling tax obligations, they are not interchangeable. EINs are specifically assigned to businesses, whereas TINs encompass a broader range of identification numbers, including those used by individuals. Recognizing these distinctions can significantly impact how organizations manage their tax responsibilities and business operations.
Key insights highlight that:
- EINs are vital for entities with employees, corporations, and partnerships.
- Individuals often utilize their Social Security Numbers as TINs.
- The application processes for both identifiers are straightforward but require careful attention to detail to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
By understanding when to use an EIN versus a TIN, businesses can streamline their operations and avoid potential penalties associated with tax misreporting.
Ultimately, grasping the nuances of EINs and TINs not only facilitates better compliance but also empowers businesses to optimize their tax strategies effectively. Whether establishing a new company or managing an existing one, ensuring the correct use of these identifiers is paramount. Organizations should prioritize clarity in their tax identification processes to enhance operational success and maintain regulatory adherence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Employer Identification Number (EIN)?
An Employer Identification Number (EIN) is a unique nine-digit code assigned by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for tax purposes, commonly referred to as a Federal Tax Number.
What are the main uses of an EIN?
EINs are used for various business operations, including hiring employees, opening bank accounts, obtaining credit, and filing taxes, particularly for e-commerce and gaming enterprises in the U.S.
What is a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)?
A Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is a broader term that encompasses various identification numbers used by the IRS, including EINs.
Are EIN and TIN the same?
No, EIN and TIN are not the same; EIN is a specific type of TIN used primarily for businesses.
Why is obtaining a TIN important for businesses in the U.S.?
Obtaining a TIN is crucial for businesses to comply with tax regulations, as it is necessary for filing taxes and meeting IRS requirements. Without a TIN, individuals cannot file taxes, which may lead to penalties.
What sectors particularly need to be aware of EINs and TINs?
Businesses in the e-commerce and gaming sectors need to be particularly aware of EINs and TINs for tax reporting and compliance.