Introduction
The choice of company suffix can significantly shape the trajectory of an e-commerce venture. Entrepreneurs often face uncertainty when deciding between an LLC and an Inc. Each structure presents distinct advantages and disadvantages that can impact various aspects, from taxation to regulatory obligations. Understanding these differences is essential for aligning business goals with operational needs. Entrepreneurs should consider several factors when navigating this critical decision, as the right choice can empower their growth in a competitive online marketplace.
Define Company Suffixes: LLC vs. Inc.
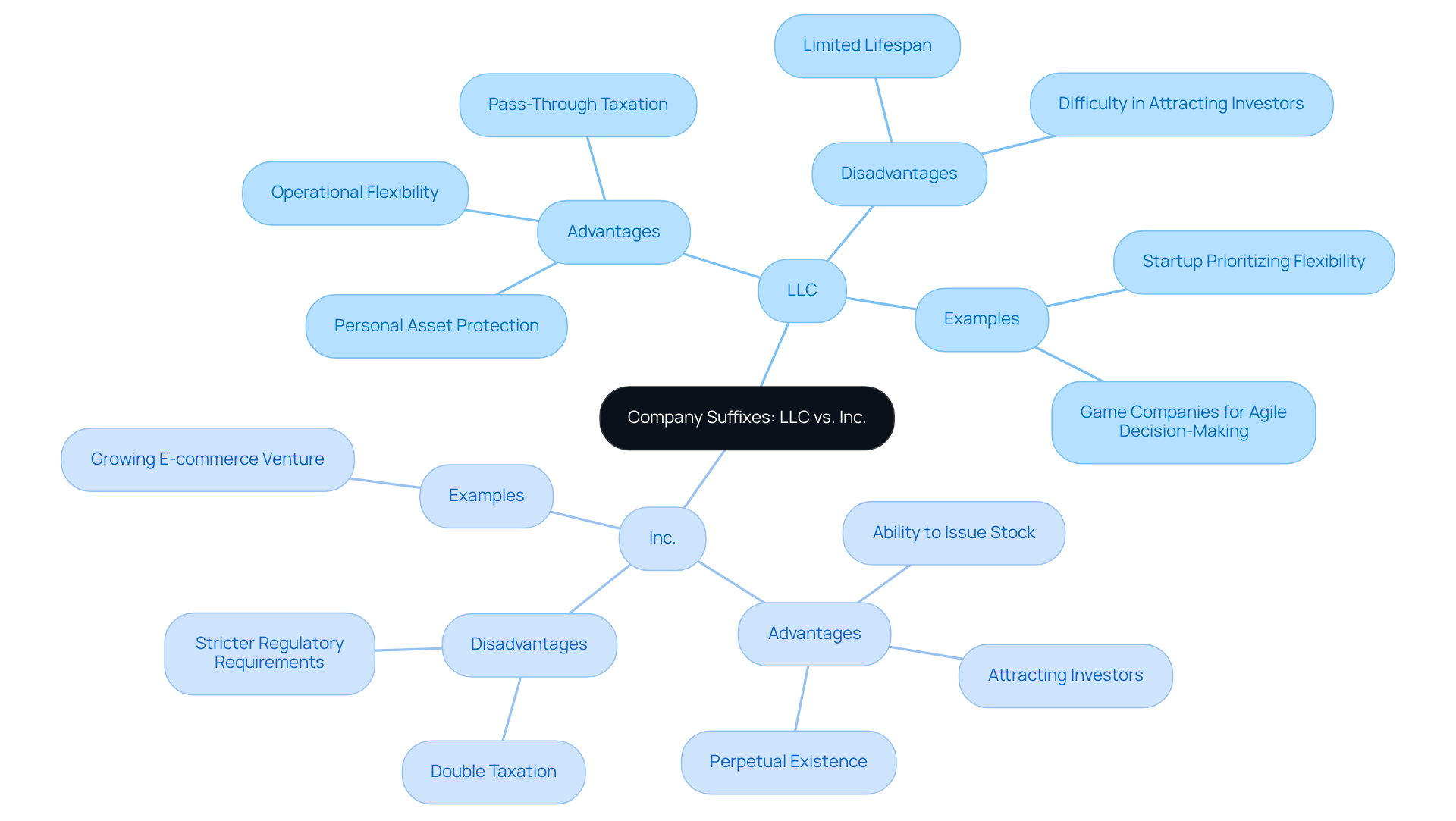
The suffixes ‘LLC’ and ‘Inc.’ denote distinct organizational structures in the United States, each carrying unique implications for entrepreneurs. An LLC, or Limited Liability Company, merges the operational flexibility of a partnership with the liability protection characteristic of a business entity. This structure safeguards members’ personal assets from corporate liabilities, making it an attractive option for many startups. In contrast, ‘Inc.’ indicates that a business is a corporation, a more formal entity capable of issuing stock and owned by shareholders. Corporations generally encounter stricter regulatory requirements and double taxation on profits, which can significantly influence financial planning.
For online retail entrepreneurs, grasping these distinctions is crucial. An LLC provides ease of setup and management, with fewer formalities and the advantage of pass-through taxation, allowing profits to be reported on personal tax returns. Conversely, corporations, while enabling capital raising through stock issuance, necessitate compliance with more complex regulations, including annual meetings and meticulous record-keeping.
Real-world examples illustrate these differences:
- A startup opting for an LLC structure may prioritize flexibility and personal asset protection.
- A growing e-commerce venture seeking to attract investors might choose incorporation to leverage stock options.
- Game companies may find that an LLC structure facilitates more agile decision-making and reduces operational costs, which can be vital in a competitive market.
Ultimately, the decision between LLC and Inc. should align with the entrepreneur’s objectives, funding strategies, and desired level of operational complexity. Consulting with experts, such as Social Enterprises, can provide valuable insights into these company suffixes, ensuring informed decisions that influence the long-term success of a business.
Compare Advantages and Disadvantages of LLCs and Incs
When comparing LLCs and corporations (Inc.), distinct advantages and disadvantages emerge that are particularly relevant for e-commerce entrepreneurs.
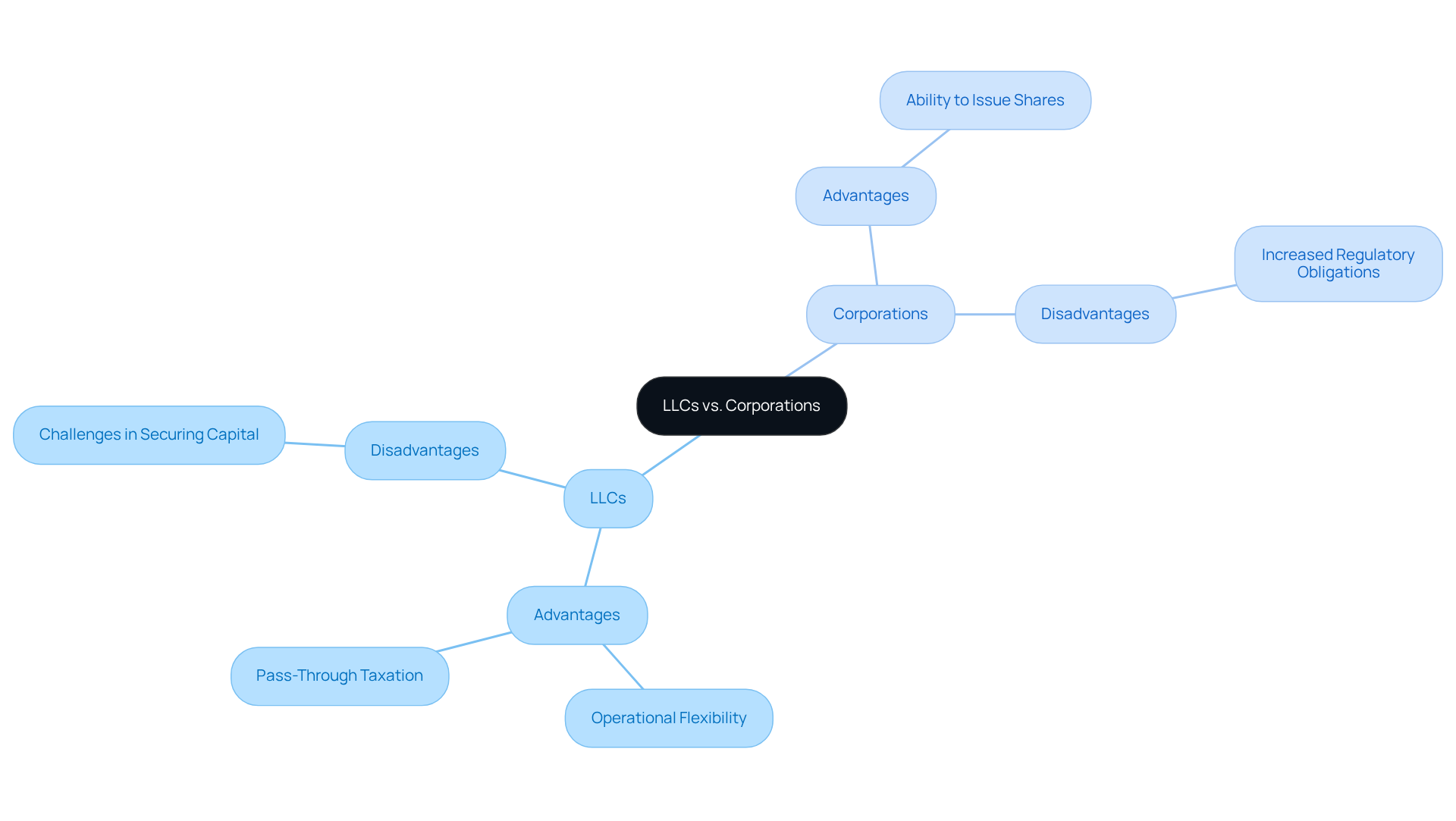
- LLCs are often preferred for their operational flexibility and reduced formalities, which simplify management.
- They benefit from pass-through taxation, allowing profits to be taxed solely at the individual level and avoiding the double taxation commonly associated with corporations.
- However, LLCs may encounter challenges in securing capital, as they lack the ability to issue shares to attract investors as readily as corporations can.
On the other hand, corporations can leverage their ability to issue shares, a significant advantage for businesses seeking growth and investment.
- This potential for expansion, however, is accompanied by increased regulatory obligations, including mandatory board meetings and stringent record-keeping requirements.
For online business owners, understanding this comparison is crucial, as they must weigh the operational simplicity of an LLC against the growth opportunities presented by a corporate structure.
Examine Legal and Tax Implications of LLCs and Incs
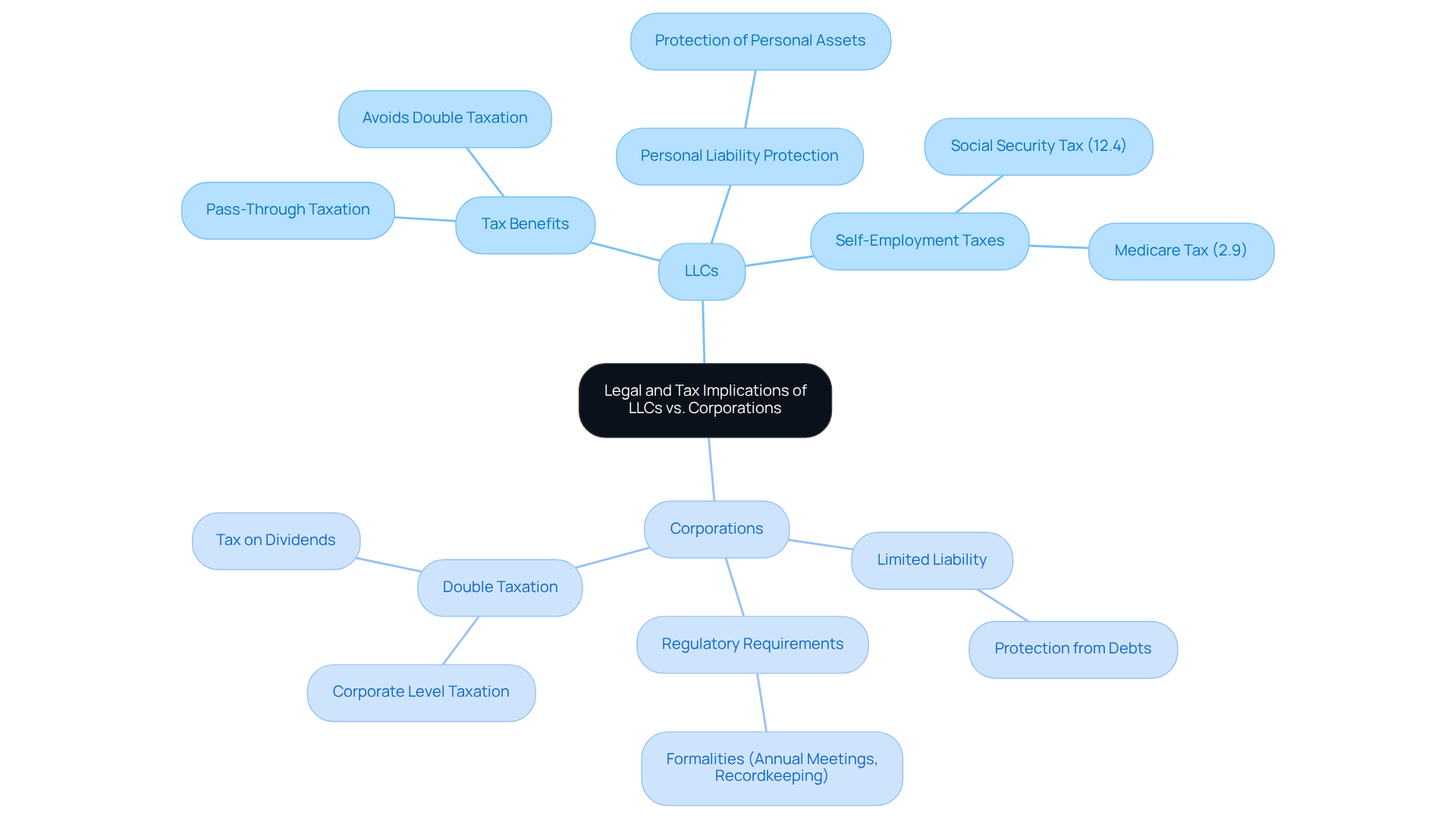
The choice between forming an LLC or a corporation has significant legal and tax implications, especially for e-commerce businesses. LLCs benefit from pass-through taxation, which allows profits and losses to be reported on the owners’ personal tax returns instead of being taxed at the entity level. This structure can result in substantial tax savings for small business owners, as it avoids the double taxation faced by corporations – where profits are taxed at the corporate level and again as dividends to shareholders.
From a legal standpoint, LLCs provide robust personal liability protection, ensuring that members’ personal assets are shielded from debts and obligations. However, LLC members must also take into account self-employment taxes, which include a 12.4% tax for Social Security and a 2.9% tax for Medicare, thereby affecting their overall tax burden.
In contrast, while corporations also offer limited liability, they are subject to more rigorous regulatory requirements, including formalities such as annual meetings and comprehensive recordkeeping. The complexities of state regulations governing LLCs can introduce uncertainty for online businesses operating across multiple states, resulting in additional paperwork and inconsistent treatment. This complexity can pose challenges for online retailers, making the LLC structure a more appealing option for many entrepreneurs seeking simplicity and efficiency in their operations.
Assess Suitability of LLC vs. Inc. for E-commerce Ventures
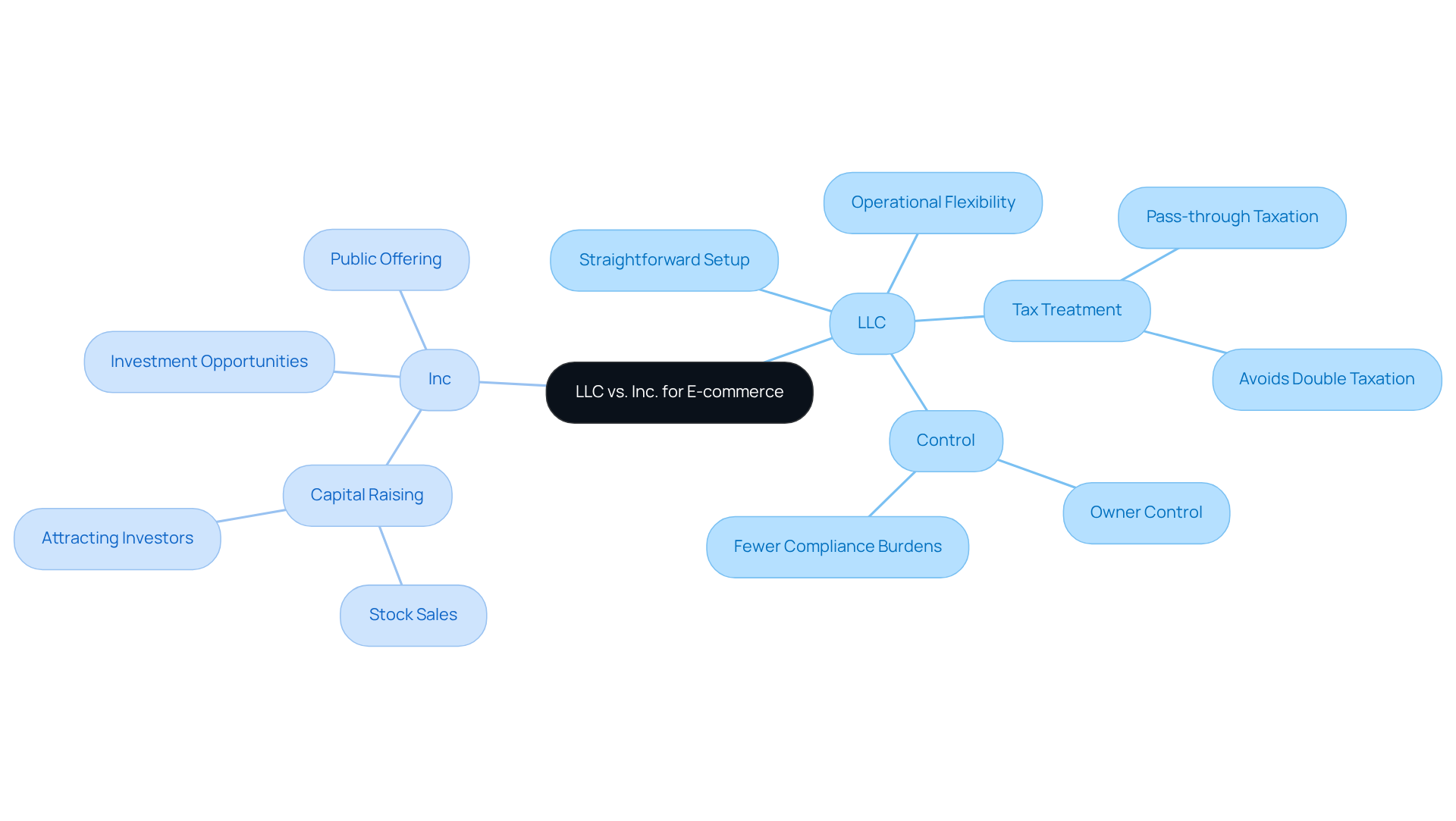
When evaluating the suitability of LLCs versus Incs for online business ventures, several critical factors must be considered. LLCs are frequently preferred by small to medium-sized online retail businesses due to their operational flexibility, straightforward setup, and advantageous tax treatment. They empower owners to maintain control without the extensive regulatory compliance burdens associated with corporations.
Conversely, larger online retail companies that seek significant investment or plan to go public may find the corporate structure of an Inc. more advantageous, as it facilitates capital raising through stock sales. For example, numerous successful e-commerce entrepreneurs have chosen LLCs to safeguard personal assets while benefiting from pass-through taxation, thereby avoiding the double taxation that corporations encounter.
Ultimately, the choice between LLC and Inc. should reflect the entrepreneur’s vision for growth, funding needs, and operational preferences, ensuring that the selected structure aligns with their long-term business objectives.
Conclusion
Choosing the right business structure is a pivotal decision for e-commerce entrepreneurs. Understanding the differences between LLCs and corporations (Inc.) is essential for establishing a strong foundation. Each suffix signifies a distinct organizational framework that influences liability, taxation, and operational complexities. By recognizing the unique advantages and challenges associated with both LLCs and Incs, entrepreneurs can make informed choices that align with their business goals.
This article explores the specific characteristics of LLCs and corporations, highlighting their respective benefits and drawbacks. LLCs provide flexibility, ease of management, and favorable tax treatment through pass-through taxation, making them particularly appealing for small to medium-sized businesses. Conversely, corporations can attract significant investment through stock issuance but are subject to stringent regulatory requirements and the burden of double taxation. Real-world examples illustrate how varying business needs and growth aspirations can guide the choice between these two structures.
Ultimately, the decision between LLC and Inc. should reflect an entrepreneur’s vision for their business. Factors such as funding strategies, operational preferences, and long-term objectives must be considered. By carefully evaluating these elements and seeking expert advice, e-commerce entrepreneurs can select the most suitable structure that not only protects their personal assets but also positions their business for future success. Making an informed choice in this regard transcends mere compliance; it lays the groundwork for sustainable growth and resilience in a competitive market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do the suffixes ‘LLC’ and ‘Inc.’ signify in a business context?
‘LLC’ stands for Limited Liability Company, which combines the operational flexibility of a partnership with liability protection. ‘Inc.’ indicates that a business is a corporation, a formal entity that can issue stock and is owned by shareholders.
What are the main advantages of forming an LLC?
An LLC offers ease of setup and management, personal asset protection from corporate liabilities, and pass-through taxation, allowing profits to be reported on personal tax returns.
What are the characteristics of a corporation indicated by ‘Inc.’?
A corporation can issue stock, is owned by shareholders, faces stricter regulatory requirements, and is subject to double taxation on profits.
Why is it important for online retail entrepreneurs to understand the differences between LLC and Inc.?
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed decisions about business structure, which can impact operational flexibility, regulatory compliance, and financial planning.
Can you give examples of when a business might choose LLC or Inc.?
A startup may choose an LLC for flexibility and personal asset protection, while a growing e-commerce venture might opt for incorporation to attract investors through stock options.
What are the operational implications of choosing an LLC over a corporation?
An LLC typically involves fewer formalities and less complex regulations compared to a corporation, which requires annual meetings and meticulous record-keeping.
How can entrepreneurs make informed decisions between LLC and Inc.?
Entrepreneurs should align their choice with their business objectives, funding strategies, and desired level of operational complexity, and may benefit from consulting with experts.