Introduction
Understanding the distinct characteristics of business structures is essential for entrepreneurs navigating the complex landscape of company formation. Many startups are increasingly leaning towards Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) due to their flexibility and tax benefits. Consequently, the choice between forming an LLC or a corporation becomes significant. Entrepreneurs must consider the challenges that arise when deciding which structure best aligns with their long-term goals. Furthermore, the features of each entity play a crucial role in influencing that decision.
Define LLC and Corporation: Key Characteristics
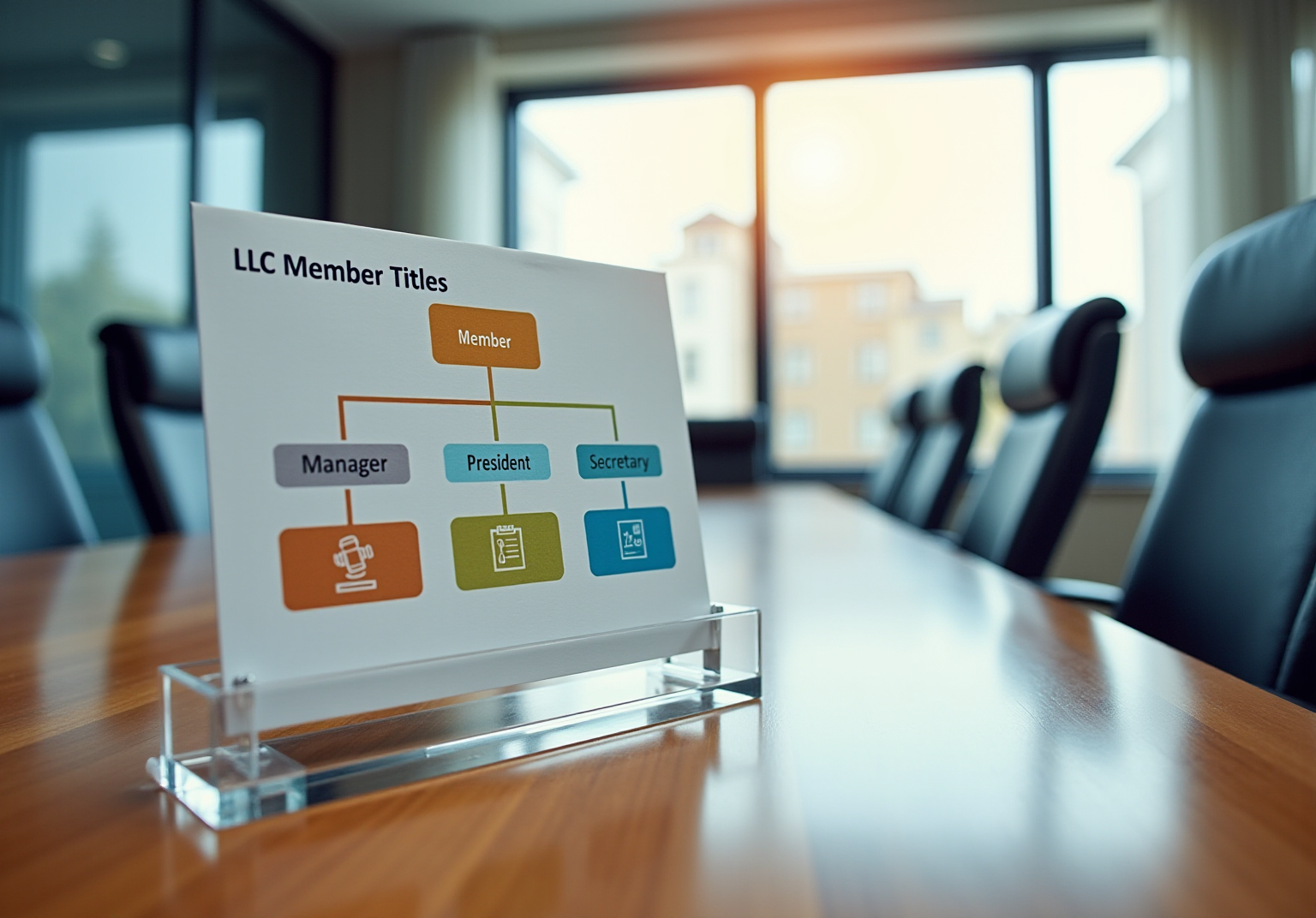
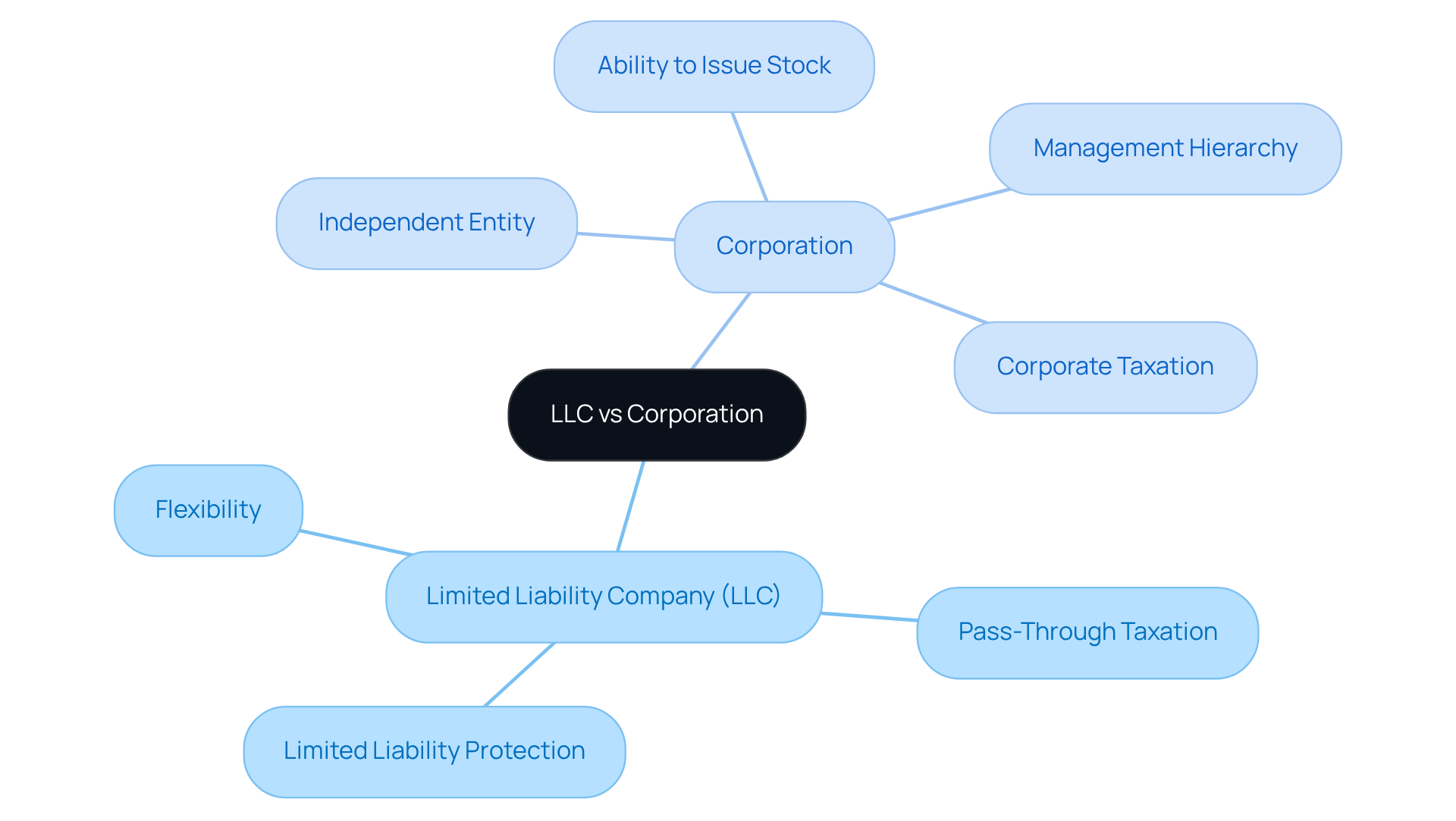
A Limited Liability Company (LLC) represents a flexible organizational structure that merges the advantages of both enterprises and partnerships. LLCs provide limited liability protection to their owners, known as members, which safeguards personal assets from business debts and liabilities. Additionally, this structure allows for pass-through taxation, meaning profits are taxed solely at the individual level, thereby avoiding the double taxation often associated with corporations.
In contrast, a corporation is a more formal entity that exists independently of its owners, referred to as shareholders. Corporations have the ability to issue stock, maintain a defined management hierarchy, and are subject to corporate taxation, which can lead to double taxation on profits.
As of 2026, a significant number of companies are opting for LLCs due to their flexibility and simplified tax arrangements, making them particularly appealing for startups and small ventures. Understanding the difference between LLC and Inc. is crucial for entrepreneurs as they evaluate their formation options, ensuring alignment with their long-term objectives and operational needs.
Explore the Origins and Evolution of LLCs and Corporations
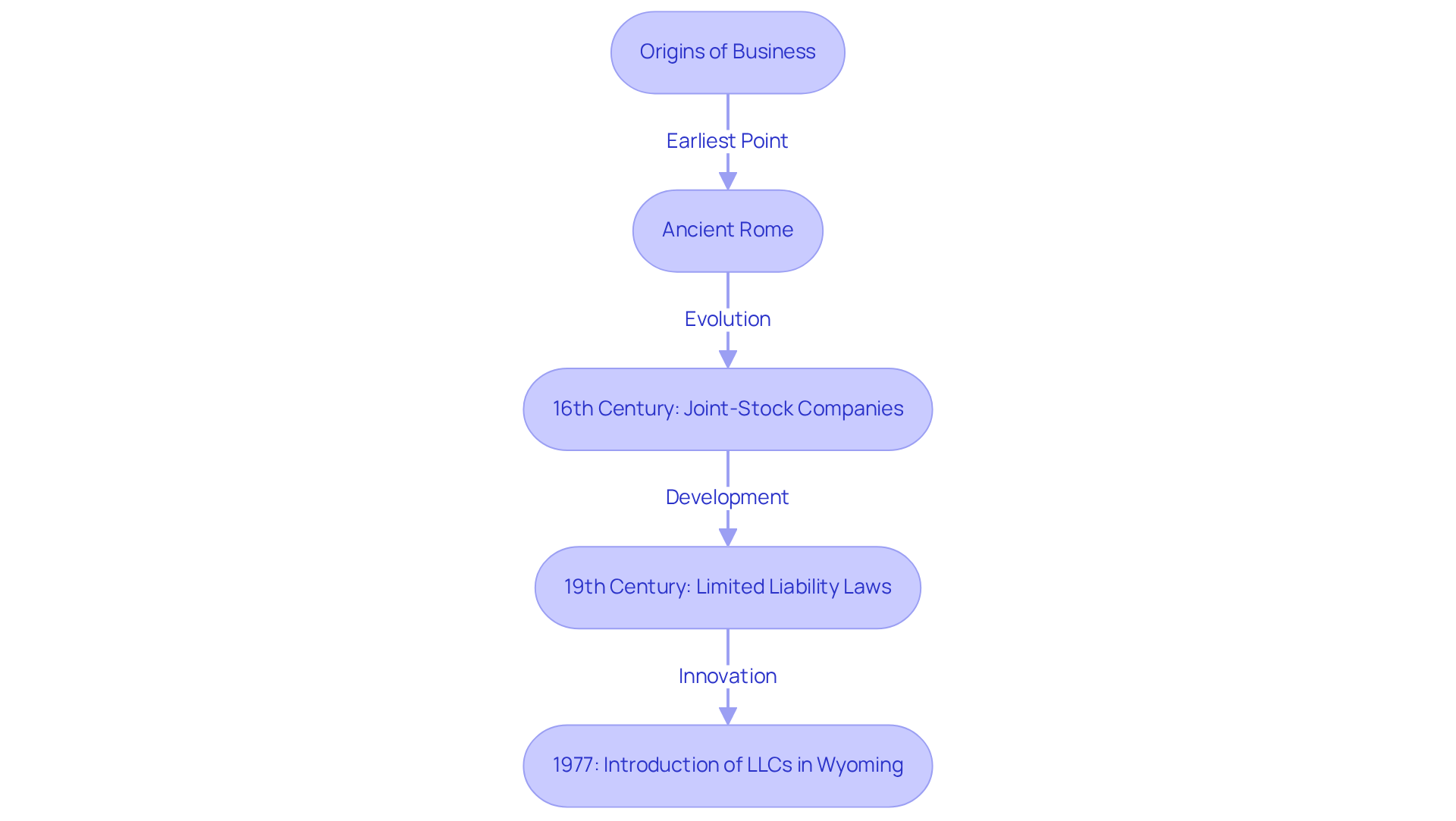
The Limited Liability Company (LLC) was first introduced in the United States in Wyoming in 1977. This hybrid organizational structure combines the operational flexibility of a partnership with the liability protection of a corporation. This innovation emerged to meet the evolving needs of entrepreneurs who sought a more adaptable entity in a rapidly changing business environment.
In contrast, the concept of businesses has a much longer lineage, tracing back to ancient Rome and evolving through the establishment of joint-stock companies in the 16th century. The 19th century marked a significant transformation in the business landscape, particularly with the introduction of limited liability laws. These laws allowed shareholders to limit their financial risk, fundamentally altering the dynamics of business ownership.
Understanding these historical developments is crucial for entrepreneurs today. It sheds light on the legal frameworks that shape contemporary business operations and informs the strategic choices available in the current marketplace.
Analyze the Differences: LLC vs. Corporation
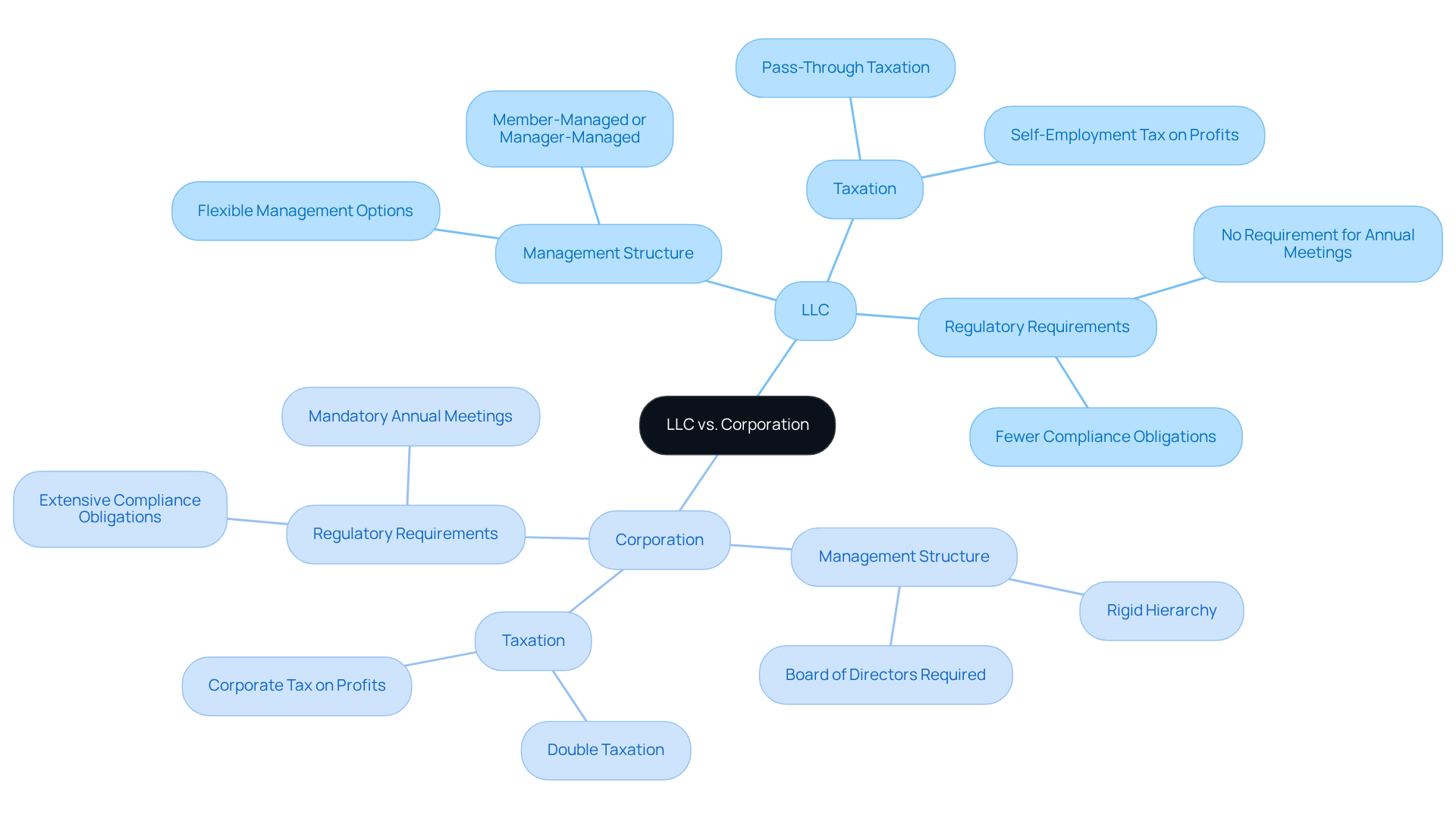
To understand what’s the difference between LLC and Inc, one must consider their management structures, taxation, and regulatory requirements. LLCs offer enhanced flexibility in management, allowing members to opt for either a member-managed or manager-managed framework. In contrast, traditional corporations typically adhere to a more rigid hierarchy, necessitating a board of directors and corporate officers.
Taxation differences are also significant; LLCs benefit from pass-through taxation, meaning profits are taxed only at the individual level. Conversely, corporations face double taxation-first at the corporate level and again when dividends are distributed to shareholders. Furthermore, LLCs generally have fewer ongoing compliance obligations, such as annual meetings and extensive record-keeping, which simplifies management for small business owners.
For international entrepreneurs looking to establish a venture in the U.S., understanding what’s the difference between LLC and Inc is crucial as they evaluate their goals and operational preferences. Consulting with specialists, such as Social Enterprises, can provide tailored guidance on selecting the appropriate organizational structure, ensuring compliance with tax regulations, and navigating the complexities of company formation. Common inquiries often include determining which type of company best suits specific commercial needs and how to effectively manage tax obligations, both of which can be addressed through expert consultation.
Identify Similarities: Common Features of LLCs and Corporations
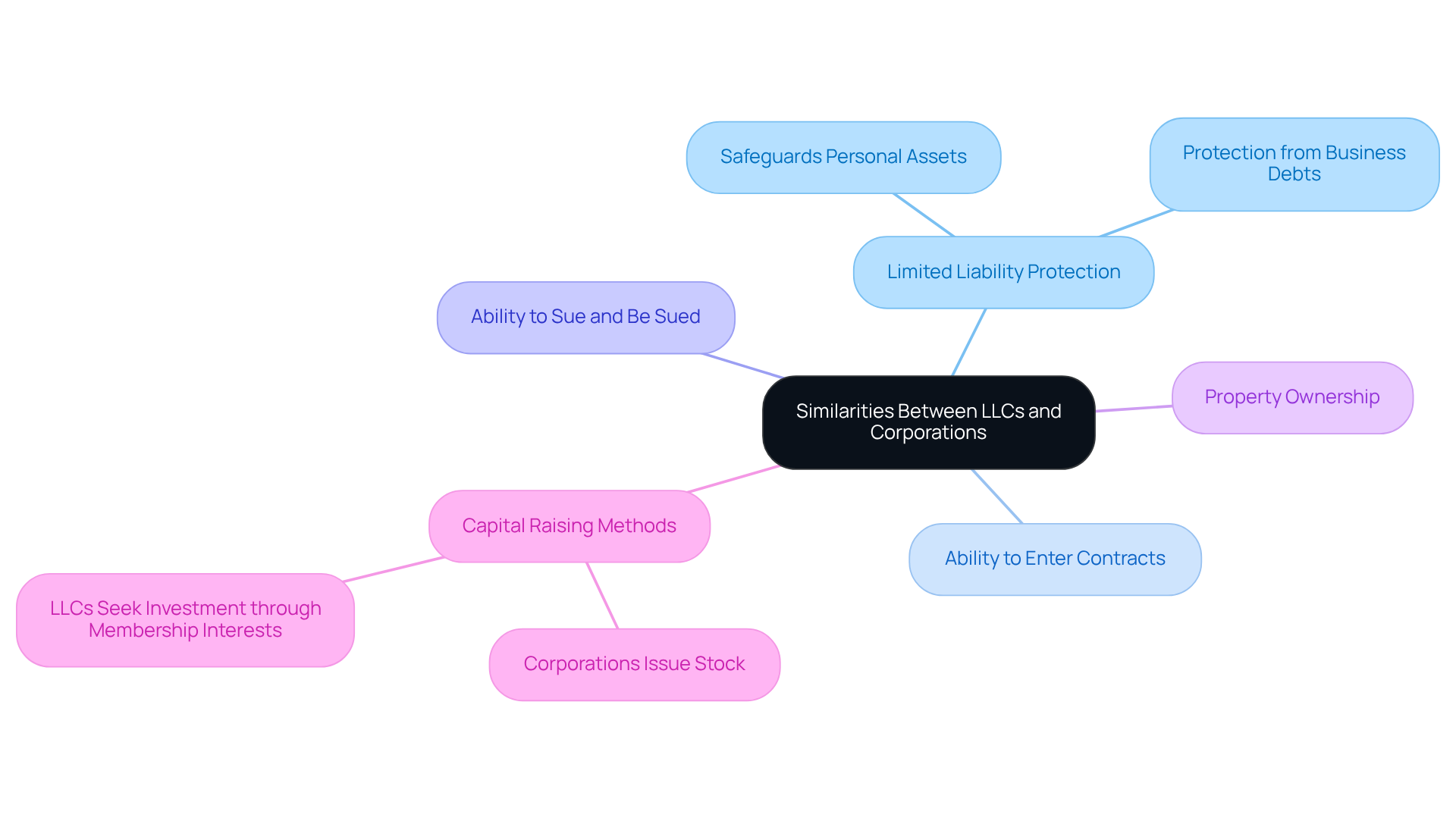
Understanding what’s the difference between llc and inc is crucial for international e-commerce entrepreneurs, as both share several key features despite their differences. Both structures provide limited liability protection, meaning that owners are not personally liable for the debts and obligations of the business. This protection is a significant advantage, as it safeguards personal assets from business risks.
Moreover, both limited liability companies and corporations can enter into contracts, sue and be sued, and hold property in their own names. They also possess the ability to raise capital, although the methods vary; corporations can issue stock, while limited liability companies may seek investment through membership interests.
Understanding what’s the difference between llc and inc is crucial for entrepreneurs as they evaluate their options and consider the level of protection and operational capabilities they require, especially regarding company formation and tax compliance in the U.S. for startups and e-commerce ventures.
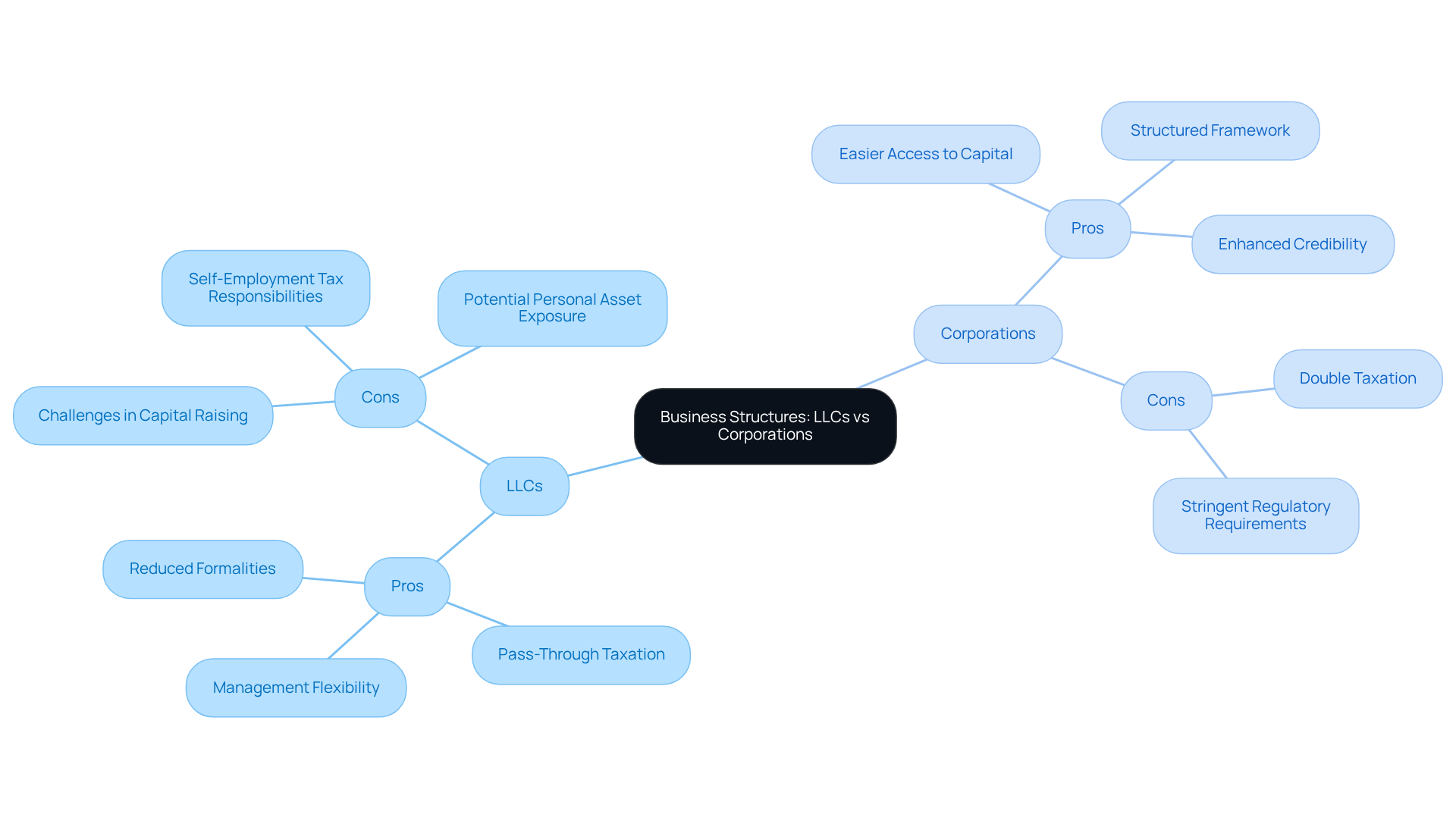
Evaluate Pros and Cons: Benefits and Drawbacks of LLCs and Corporations
When assessing business structures, limited liability companies (LLCs) present notable advantages, including management flexibility, pass-through taxation, and reduced formalities. These features make LLCs particularly appealing for small enterprises. For example, LLCs can circumvent double taxation and allow for profit and loss allocation based on criteria beyond mere ownership percentage. Furthermore, if you are the sole owner of a U.S. LLC, the IRS classifies the LLC as a “disregarded entity,” meaning that the LLC itself does not incur tax liabilities; instead, you, as an individual, report taxes on Form 1040-NR.
However, LLCs often encounter challenges in capital raising, as they lack the ability to issue stock, which can limit their attractiveness to potential investors. In contrast, corporations benefit from easier access to capital through stock issuance, a structured framework that enhances credibility, and the potential to attract institutional investors. Recent statistics indicate that corporations have a higher success rate in raising capital compared to LLCs, a crucial consideration for entrepreneurs.
Despite these advantages, businesses must also contend with drawbacks, such as double taxation on profits and more stringent regulatory requirements. Entrepreneurs should carefully evaluate these pros and cons in light of their specific business objectives, funding needs, and operational preferences to determine the most suitable structure for their ventures. For instance, while LLCs may be ideal for those prioritizing operational simplicity and favorable tax treatment, corporations may be more appropriate for those seeking substantial investment opportunities. As Nellie Akalp, CEO of CorpNet.com, states, “The best option depends on each individual owner’s current needs and future plans.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) and corporations is essential for entrepreneurs navigating their business formation options. Each structure presents unique benefits and challenges that can significantly impact operational efficiency, tax obligations, and long-term strategic goals. By grasping these differences, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and aspirations.
This article highlights the key characteristics of LLCs and corporations, emphasizing their management structures, taxation methods, and regulatory requirements. LLCs are notable for their flexibility and pass-through taxation, while corporations offer a more formal structure with the capacity to raise capital through stock issuance. The historical context is also explored, revealing how these entities evolved to meet the changing demands of the business landscape.
Ultimately, the choice between an LLC and a corporation should be guided by an entrepreneur’s unique objectives, funding needs, and operational preferences. As the business environment continues to evolve, staying informed about the advantages and disadvantages of each structure will empower entrepreneurs to position their ventures for success. Engaging with experts and conducting thorough research can further enhance decision-making, ensuring that the chosen entity aligns with both current requirements and future ambitions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Limited Liability Company (LLC)?
An LLC is a flexible organizational structure that combines the benefits of both corporations and partnerships. It provides limited liability protection to its owners, known as members, safeguarding their personal assets from business debts and liabilities. Additionally, LLCs benefit from pass-through taxation, where profits are taxed at the individual level, avoiding double taxation.
How does a corporation differ from an LLC?
A corporation is a more formal entity that exists independently of its owners, referred to as shareholders. Corporations can issue stock, have a defined management hierarchy, and are subject to corporate taxation, which can lead to double taxation on profits.
Why are many companies opting for LLCs as of 2026?
Many companies are choosing LLCs due to their flexibility and simplified tax arrangements, making them particularly appealing for startups and small ventures.
When and where was the LLC first introduced?
The Limited Liability Company (LLC) was first introduced in the United States in Wyoming in 1977.
What historical developments led to the creation of LLCs?
LLCs emerged to meet the evolving needs of entrepreneurs for a more adaptable business entity. The concept of businesses dates back to ancient Rome, with significant developments in the 16th century with joint-stock companies and the introduction of limited liability laws in the 19th century, which allowed shareholders to limit their financial risk.
Why is it important for entrepreneurs to understand the differences between LLCs and corporations?
Understanding the differences is crucial for entrepreneurs as it helps them evaluate their formation options and ensures alignment with their long-term objectives and operational needs.